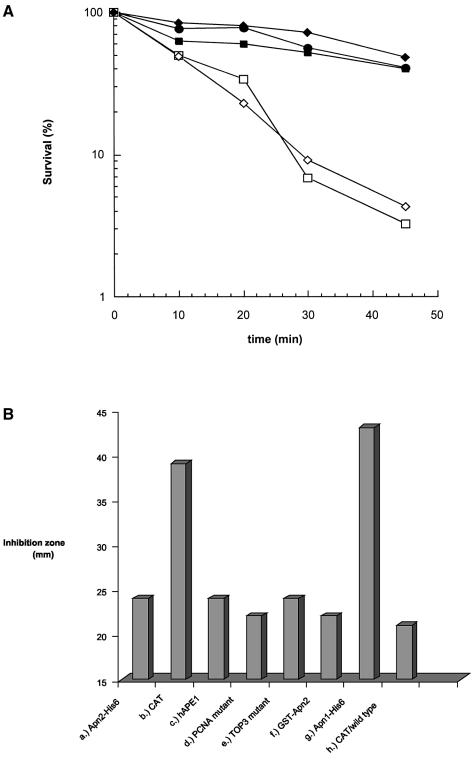
Figure 5.
(A) Complementation of MMS sensitivity of the apn1Δapn2Δ (PO60) strain with wild-type S.pombe Apn2-His6 (pNBR110) (filled squares); human APE1 (pRBR113) (filled circles); and human APE2 (pNBR103) (open squares); wild-type control, leu1-32 (PO4), with control CAT expression vector (pNMT1-CAT; Invitrogen) (filled diamonds); sensitivity of apn1Δapn2Δ: (PO60) transformed with pNMT1-CAT (open diamonds). Other details are described in Materials and Methods. (B) Agar diffusion assay of complementation of apn1Δapn2Δ (PO60) and wild-type (PO4) strains as described in Materials and Methods. Data represent results from an average of three or more experiments. (a) Wild-type Apn2-His6 on plasmid pNBR110 in PO60; (b) control pNMT1-CAT plasmid in PO60; (c) human APE1 on plasmid pRBR113 in PO60; (d) Apn2-A402A403 mutation (PCNA) on plasmid pNBR114 in PO60; (e) Apn2-A456A457A458 mutation on plasmid pNBR115 in PO60; (f) wild-type GST–Apn2 on plasmid pEBR116 in PO60; (g) wild-type Apn1-His6 on plasmid pNBR117 in PO60; (h) pNMT1-CAT plasmid in PO4