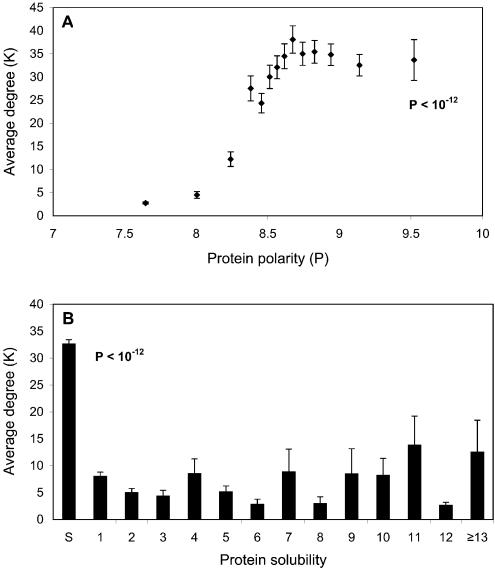
Figure 4.
Relationships between average degree and protein polarity, and solubility. (A) Protein polarity is determined as the average polarity of all its composing amino acids. Proteins are binned into 14 groups with approximately the same number of proteins in each group. The P value, calculated by the Mann–Whitney test (a non-parametric T test) (46), measures the difference between the protein groups of highest and lowest polarities. (B) The number of trans-membrane helices is predicted by TMHMM server 2.0. The labels on the x-axis: S, Soluble proteins; the number means different classes of proteins with corresponding number of trans-membrane helices; ≥13, all the proteins with ≥13 trans-membrane helices. The P value, calculated by the Mann–Whitney test, measures the difference between soluble and trans-membrane proteins, which consists of all the proteins with trans-membrane helices.