Fig. 7.
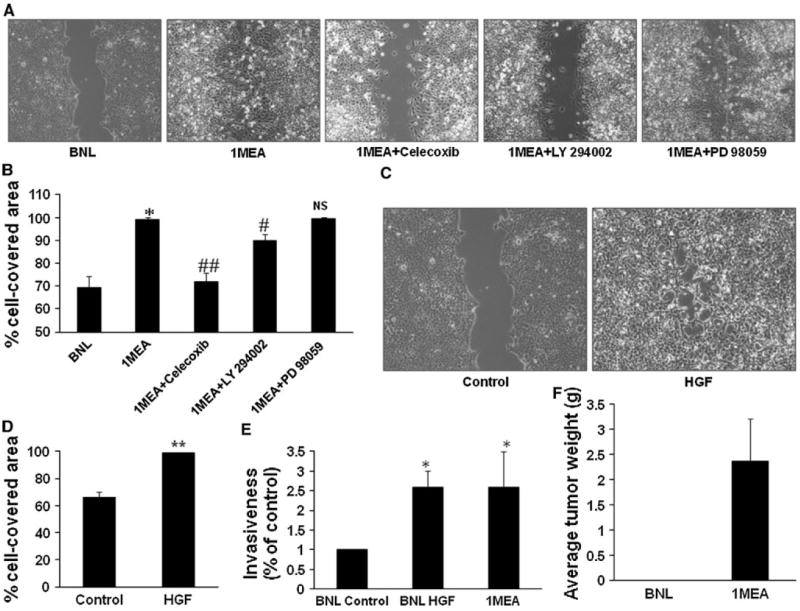
HGF promotes increased migration and invasiveness. a Migratory capacity of BNL and 1MEA cells were compared with wound healing assays. Selective inhibitors of COX-2 (1 μM celecoxib), ERK (25 μM PD 98059) and Akt (10 μM LY 294002) were used to determine the underlying mechanisms of 1MEA migration. Images (×10 objective) were taken after 24 h of culture. Images from three experiments were analyzed for percentage cell-covered area using the Wimasis Image Analysis software (Wimasis GmbH, Munich, Germany). Data is presented graphically in b. c Effect of HGF on migration was examined with wound healing assays in BNL cells. Left panel shows control cells and right panel shows cells treated with 5 ng/ml mouse hepatocyte growth factor. Image (×10 objective) was taken after 24 h. Images from three experiments were analyzed for percentage cell-covered area using the Wimasis Image Analysis software (Wimasis GmbH, Munich, Germany). Data is presented graphically in d. e Effect of HGF on BNL cell invasiveness was further examined using the in vitro Transwell double chamber invasion method. Cells that had invaded through collagen to the under surface of the insert were counted and data was analyzed and presented graphically in e. f 1MEA cells develop tumors but BNL cells do not. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01, N = 3
