Figure 4.
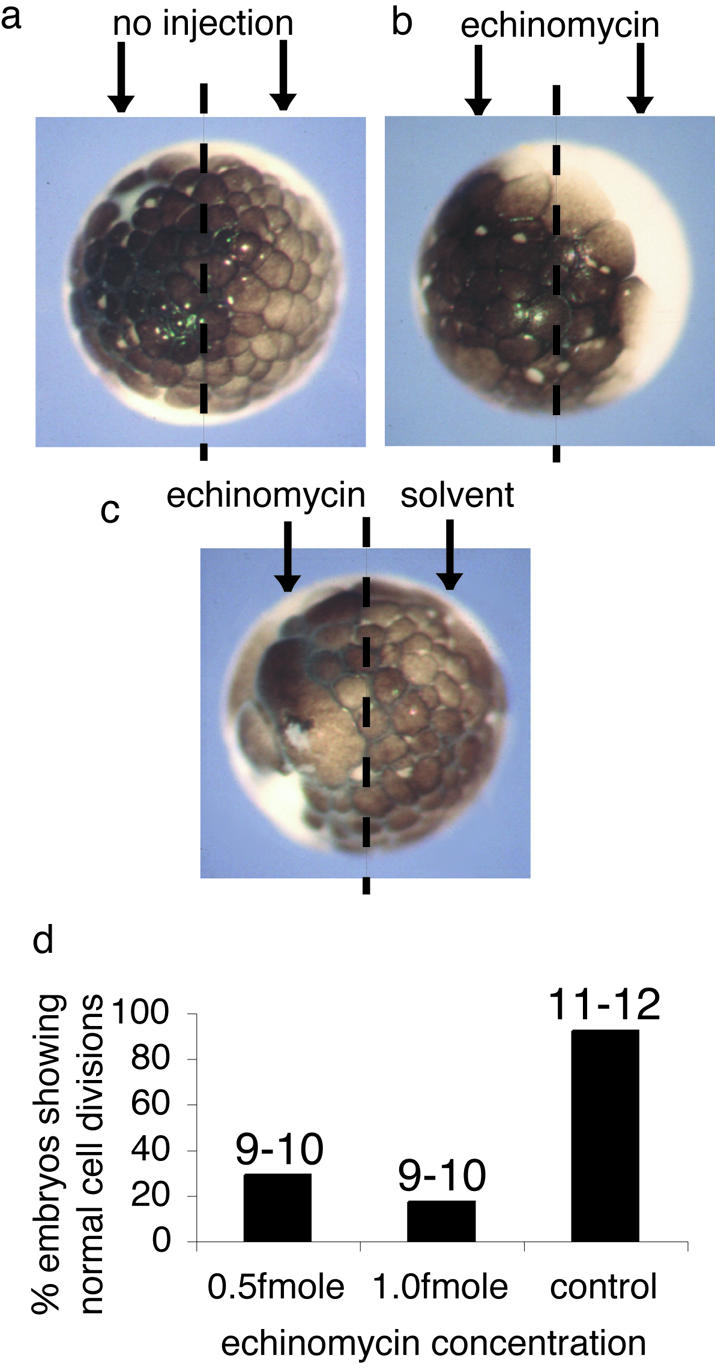
Echinomycin inhibits development of Xenopus embryos. (a) A Xenopus embryo allowed to develop for 3 h following fertilization. (b) A Xenopus embryo allowed to develop to the two-cell stage following fertilization after which 1 fmol of echinomycin was injected into each cell and embryos allowed to develop for 3 h following fertilization. (c) A Xenopus embryo allowed to develop to the two-cell stage after which 1 fmol of echinomycin was injected into one cell and solvent into the other and embryos were allowed to develop for 3 h following fertilization. Images were collected of the animal pole of the embryos (a–c). (d) One hundred embryos were allowed to develop to the two-cell stage after which 0.5 fmol of echinomycin, 1.0 fmol of echinomycin or solvent was injected into both cells and the embryos were monitored throughout development. Numbers above each bar indicate the stage of development reached by the embryos at 21 h when control embryos had progressed to stage 11–12.
