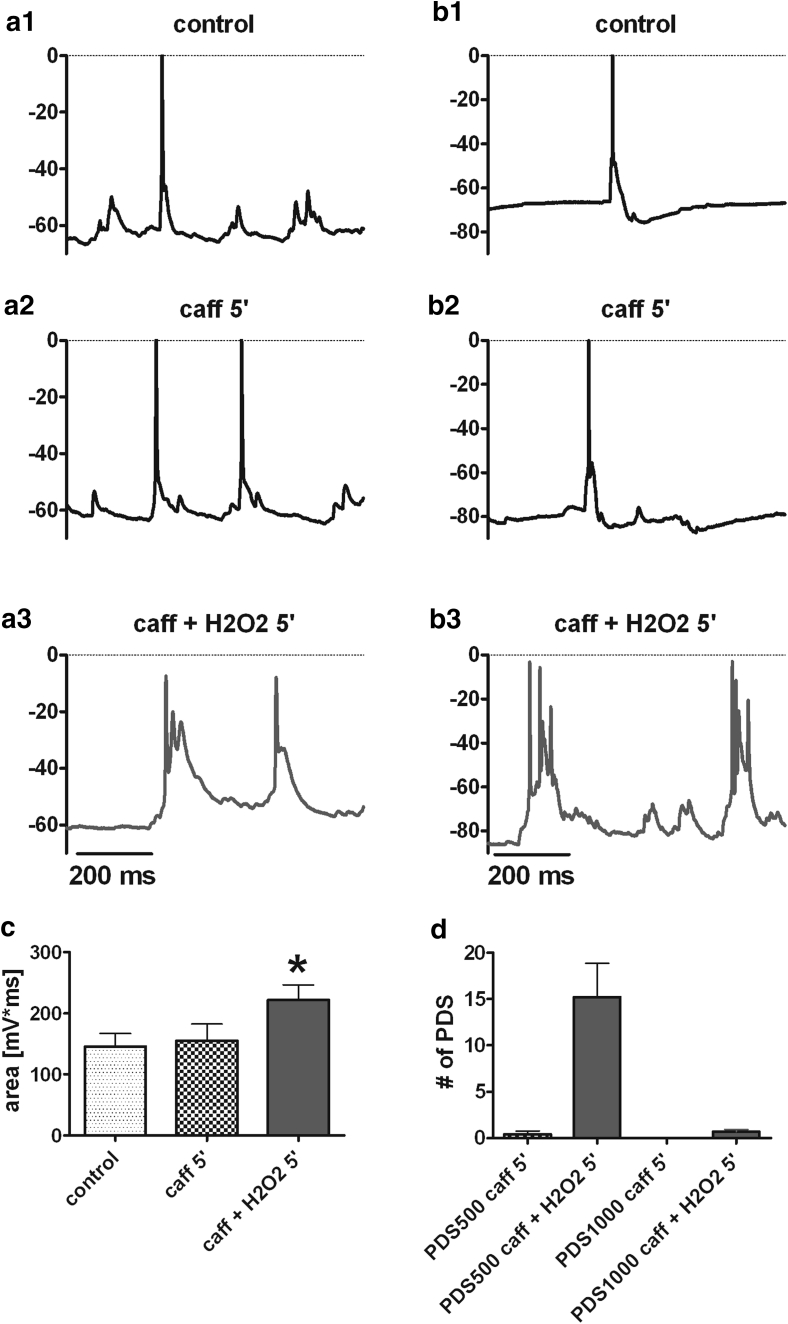
Fig. 6.
PDS induction by H2O2 in the presence of caffeine. Two examples of 3 mM H2O2-induced PDS are shown in the traces in a and b. Area and PDS1000 analysis from a total of 9 experiments is illustrated in the graphs in c an d. No alteration in discharge patterns was observed during a 5-min application of caffeine (traces in a2 and b2), but depolarization shifts emerged during a subsequent application of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2, see traces in a3 and b3). c A significant change in event area was only determined in recordings made in the presence of caffeine + H2O2 (repeated measures ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparison test, *P ≤ 0.05). d The graph illustrates that the increase in event area by H2O2 is due to the formation of a distinct number of moderately enhanced electrical events (PDS500) but only individual PDS1000 within the 2-min time frame