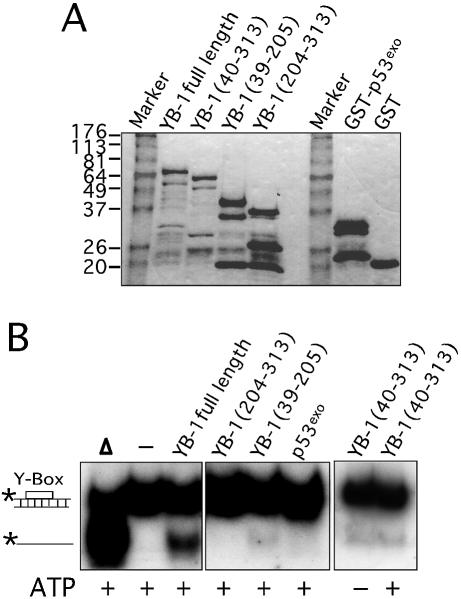
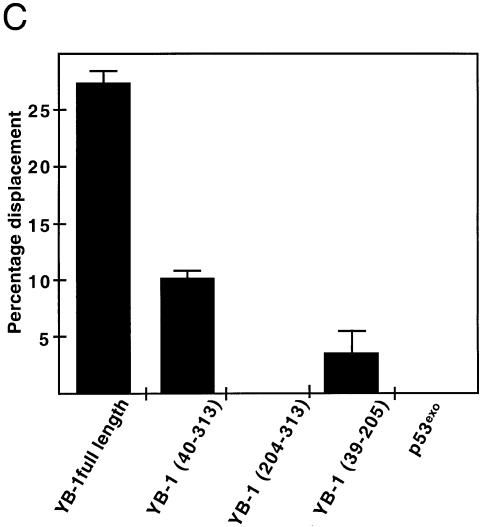
Figure 5.
Strand separation activity of different mutant YB-1 on a DNA duplex structure. (A) Characterization of the different mutant GST–YB-1 fusion proteins (before thrombin treatments) on gels stained by Coomassie. The YB-1 amino acids present in the fusion proteins are indicated above each lane. (B) The different GST-fusion proteins were cleaved with thrombin as described in the Materials and Methods and the cleaved products were used in strand displacement reactions. Approximately 40 ng of the purified YB-1, mutant YB-1 proteins or p53exo peptide (exonuclease domain) were incubated with a radioactive 22 bp duplex containing a Y-box sequence under standard conditions for helicase activity (see Materials and Methods) for 30 min at 37°C in the absence or presence of 2 mM ATP. Reactions were stopped in the appropriate dye buffer and the DNA products were analyzed on a 12% native polyacrylamide gel. The double-stranded and single-stranded structures are depicted on the left. The asterisk represents the labeled strand at its 5′ end. The triangle represents heat denatured DNA. (C) Histogram representation of the strand separation reactions performed in (B). All experiments were done in duplicate with 40 ng of purified YB-1, mutant YB-1 proteins or p53exo (exonuclease domain) in reaction buffer containing 2 mM ATP. The percentage of strand displacement is calculated by using the formula: c.p.m. of displaced strand/(c.p.m. of displaced strand + c.p.m. of double-stranded DNA) × 100. The c.p.m. was calculated for each band of the gel as indicated in Materials and Methods.