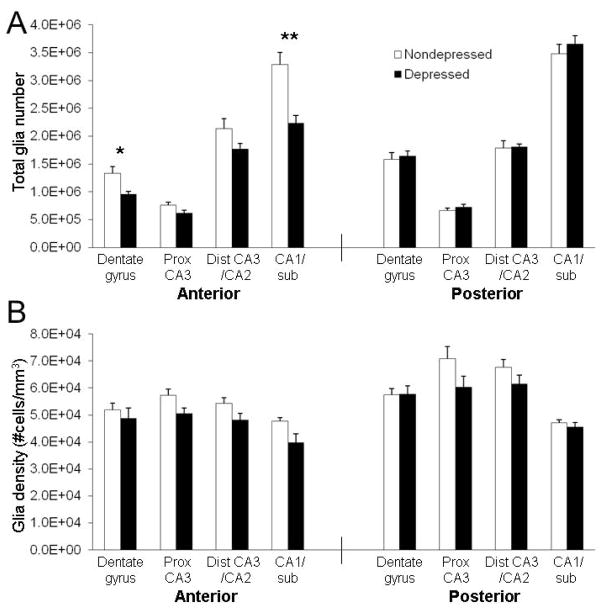
Figure 4.
Behaviorally depressed female monkeys had reduced numbers of glia in the anterior CA1 and DG. (A) Depressed monkeys had fewer glia in the anterior hippocampus (F(1,14) = 11.14, p < 0.01) and the numbers differed by subregion (F(3,42) = 8.99, p < 0.0001), with 30% fewer glia in the anterior CA1 (t(1,14) = 3.99, p = 0.001) and DG (t(1,14) = 2.85, p = 0.01). No effects were observed in the posterior hippocampus. (B) Glial density tended to be lower in the anterior hippocampus of depressed monkeys (F(1,14) = 4.15, p < 0.07), but no interaction by subregion was observed. No main effect of depression was observed for glial density in the posterior hippocampus, but the interaction by subregion was suggestive, although it did not reach significance (F(3,42) = 2.66, p = 0.06). *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01.