Fig. 2.
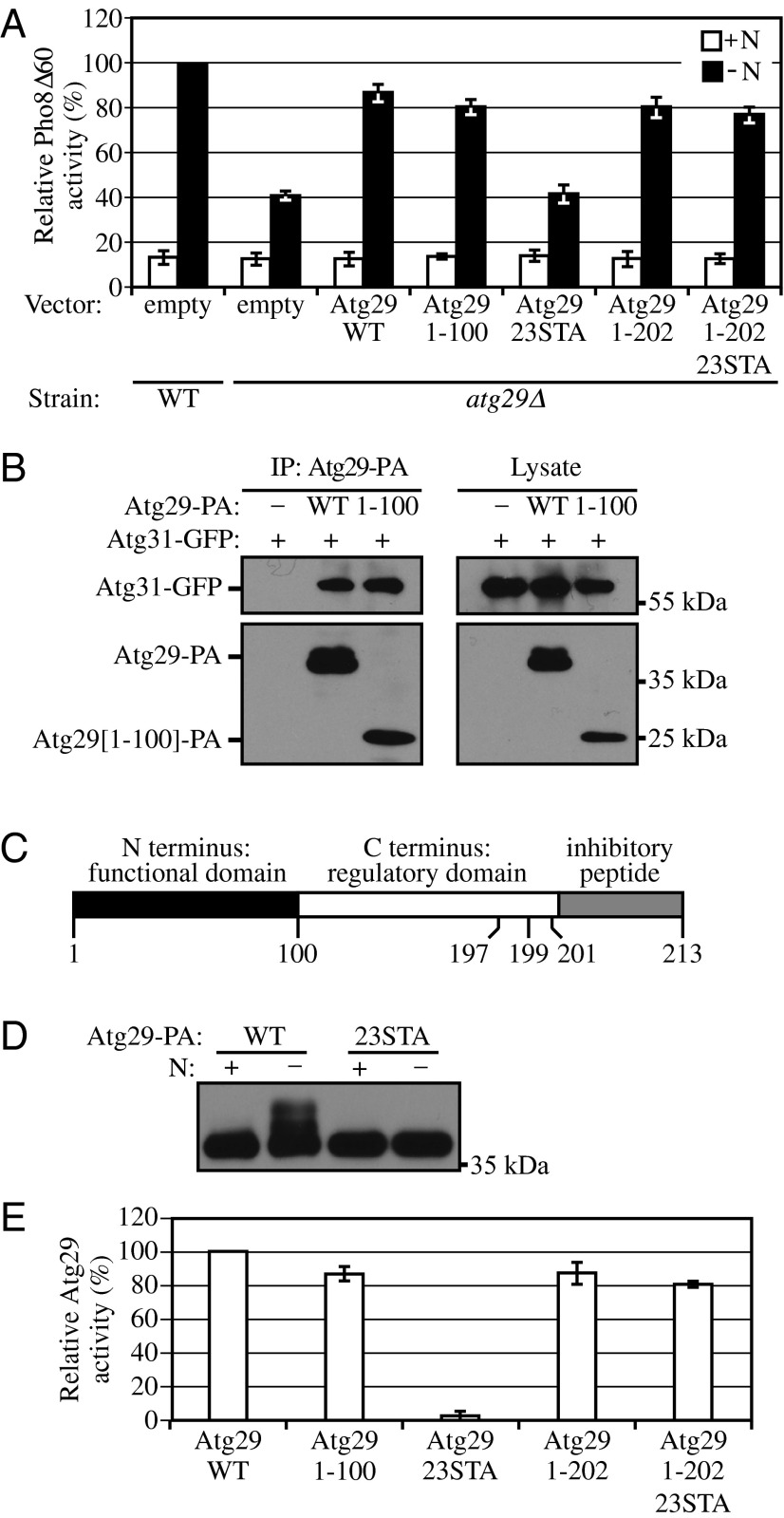
Atg29 contains distinct functional, regulatory, and inhibitory domains. (A) Pho8Δ60 WT (TN124) cells were transformed with empty vector; Pho8Δ60 atg29∆ (YIY36) cells were transformed with empty vector or a plasmid containing WT or different mutant forms of Atg29-PA as indicated. Cells were cultured in SMD to midlog phase (+N), and shifted to SD-N for 4 h. The Pho8Δ60 assay was performed as described in Materials and Methods. Error bars correspond to the SD and were obtained from three independent repeats. (B) Empty vector, plasmids encoding Atg29-PA, or Atg29[1-100]-PA was transformed into atg29∆ cells expressing Atg31-GFP (KDM1233). Cells were cultured in SMD to midlog phase, and cell lysates were prepared and incubated with IgG-Sepharose for affinity isolation as described in Materials and Methods. (C) A schematic diagram of the Atg29 protein. (D) The plasmid pAtg29-PA or pAtg29[23STA] was transformed into atg29∆ cells (HCY109). Cells were cultured in SMD, shifted to SD-N for 2 h, and analyzed by immunoblot. (E) Relative activities of different Atg29 mutants based on the results in A. The conversion from percent Pho8∆60 to relative Atg29 activity was carried out as described in the text.