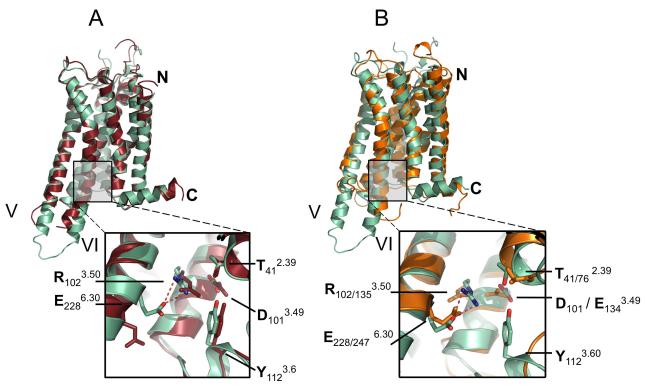
Figure 4. Comparison of A2A-StaR2-ZM241385 with A2A-T4L-ZM241385 and Rhodopsin.
(a) Superposition of A2A-StaR2-ZM241385 (pale green) with A2A-T4L-ZM241385 (dark red) using consensus Cα atoms of TM1-7, note the difference in TM5/6 helical trajectory. (Inset) Close-up of interactions across the DRY motif of A2A-StaR2 and A2A-T4L structures demonstrating ionic lock formation in the A2A-StaR2 (potential hydrogen bonds represented as dashed red lines). See also Supplementary Figure S3a. (b) Superposition of A2A-StaR2-ZM241385 (pale green) with bovine rhodopsin (orange – 1F88) using consensus Cα atoms of TM1-7. (Inset) close up of interactions across the A2A-StaR2 DRY and Rhodopsin ERY motif illustrating the similarity of the ionic lock (second subscript residue numbers refer to rhodopsin 1F88).