Figure 1. Ozone-induced oxidative stress results in epithelial injury and neutrophil inflammation.
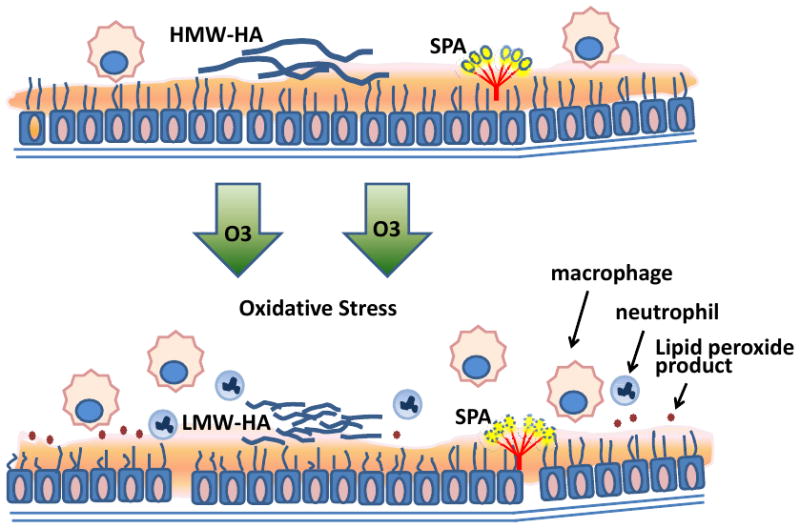
Ozone is a strong oxidant that oxidizes components in epithelial lining fluid such as SP-A and lipids producing toxic lipid peroxide products and protein adducts. The integrity of airway epithelium is impaired by ozone resulting in increased epithelial permeability. Ozone–induced oxidative stress induces fragmentation of extracellular matrix HMW-HA into LMW-HA and is associated with recruitment of neutrophils and macrophages into the airspace. (Abbreviation: HMW-HA, high molecular weight hyaluronan; LMWHA, low molecular weight hyaluronan.)
