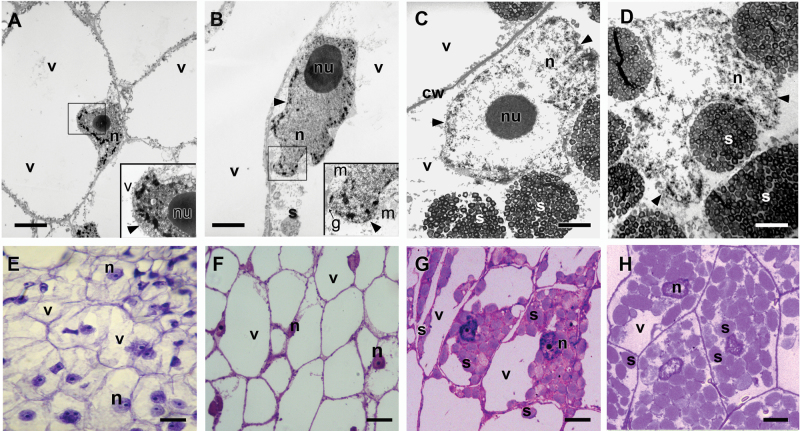
Fig. 3.
Quinoa perisperm tissue analysed by transmission electron microscopy (A–D) and light microscopy (E–H). (A–D) Changes in shape, size, and chromatin state of nuclei during seed development: (A) stage 1; (B) stage 3; (C) stage 5; (D) stage 6. (E–H) Sections of perisperm tissue corresponding to stages 1, 3, 5, and 6, respectively. Progressive changes in nuclei (disappearance of nucleolus, dispersion of chromatin) and vacuoles (disappearance), and an increase in starch accumulation (which continued until completely filling the cell lumen, occupying the vacuole space) can be observed. In each case, the figure is a representative result of observation of at least 30 whole-mounts of quinoa seeds at each stage. Abbreviations: g, Golgi apparatus; m, mitochondrion; n, nucleus; nu, nucleolus; s, compound starch grain; v, vacuole. The arrowhead indicates the nuclear membrane; Scale bars 0.5 μm (A, B); 2.5 μm (C, D); 30 μm (E–H). (This figure is available in colour at JXB online.)