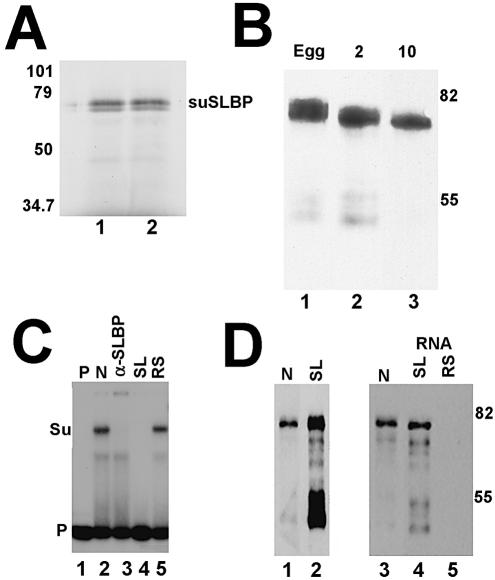
Figure 3.
The cloned suSLBP is expressed in sea urchin eggs and embryos. (A) The suSLBP was expressed by in vitro translation in a rabbit reticulocyte lysate in the presence of [35S]methionine. The proteins were resolved by gel electrophoresis and detected by autoradiography. (B) Extracts were prepared from sea urchin eggs, 2 (2-cell) and 10 h (60–100 cells) embryos in SDS. Proteins from an equal number of embryos were resolved by gel electrophoresis, transferred to nitrocellulose and the suSLBP detected by western blotting. (C) A nuclear extract from 17 h embryos was incubated with the radiolabeled stem–loop (lane 2) and the complexes resolved by native gel electrophoresis. In lane 3, affinity-purified anti-suSLBP was added to the reaction prior to electrophoresis. In lanes 4 and 5, excess stem–loop (SL) or reverse-stem (RS) was added to the probe prior to addition of the extract. Lane 1 is the probe incubated in buffer. Su is the complex formed with sea urchin SLBP. (D) A biotinylated stem–loop RNA was incubated with an extract from 5 h embryos. The proteins bound to the stem–loop (lane 2) were resolved by gel electrophoresis, and transferred to nitrocellulose. The suSLBP was detected by western blotting. Lane 1 is a nuclear extract from 17 h embryos. There was some proteolysis of the suSLBP during the purification. A nuclear extract from 17 h embryos (lane 3) was incubated with the biotinylated stem–loop (lane 4) or reverse-stem (lane 5) and the bound proteins resolved by gel electrophoresis, transferred to nitrocellulose and the suSLBP detected by western blotting.