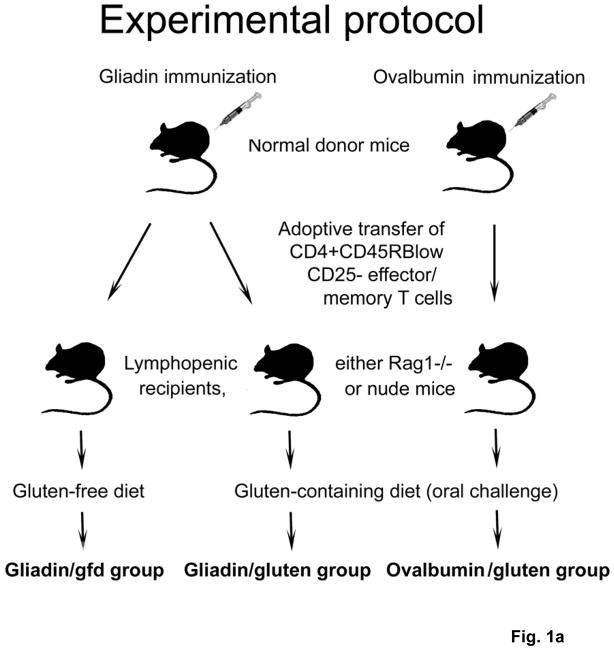
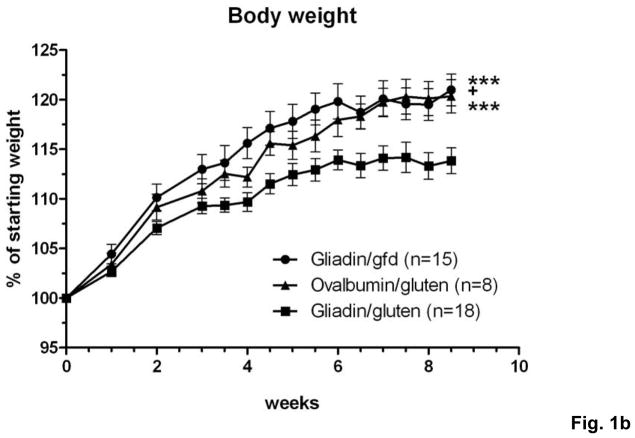
Fig. 1. Generation of a mouse model of gluten-sensitive enteropathy.
a) Splenic CD3+ T cell fractions from immunized donor mice were stained with fluorescent antibodies. Rag1−/− or nude mice were injected i.p. with 4.5×105 CD4+CD45RBlow CD25− T cells (Facs) from gliadin-immunized donors, or from ovalbumin (control)-immunized donors. After T cell transfer, recipients were either maintained on gfd (gliadin/gfd), or challenged with gluten (gliadin/gluten, ovalbumin/gluten). b) Changes in body weight in relation to individual starting weights of Rag1−/− mice (n=8–18 per group) during 8.5 weeks after transfer. Significantly lower weights in the gliadin/gluten vs. gliadin/gfd group (***p=0.001) or vs. ovalbumin/gfd (***p=0.001); while differences between gliadin/gfd vs. ovalbumin/gluten, although significant (+p<0.05), were small and transient.