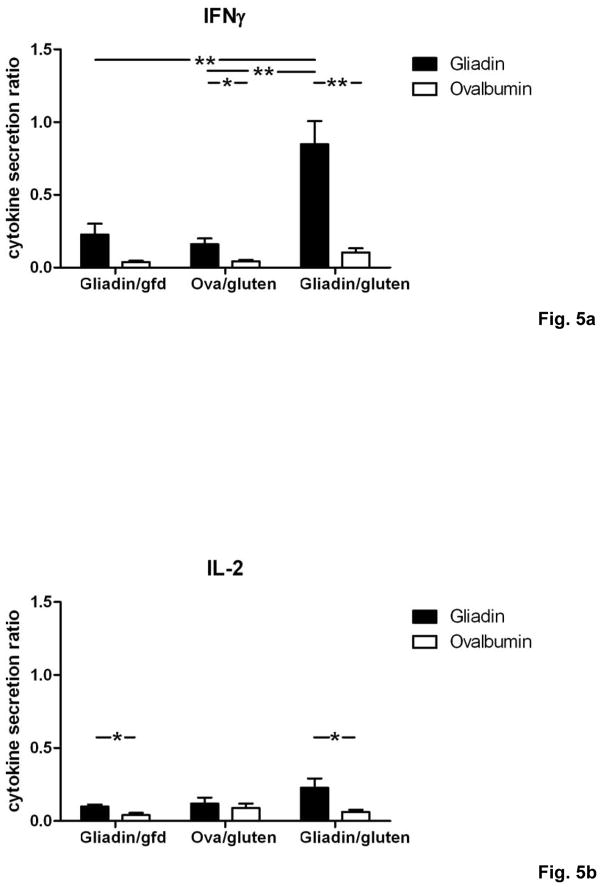
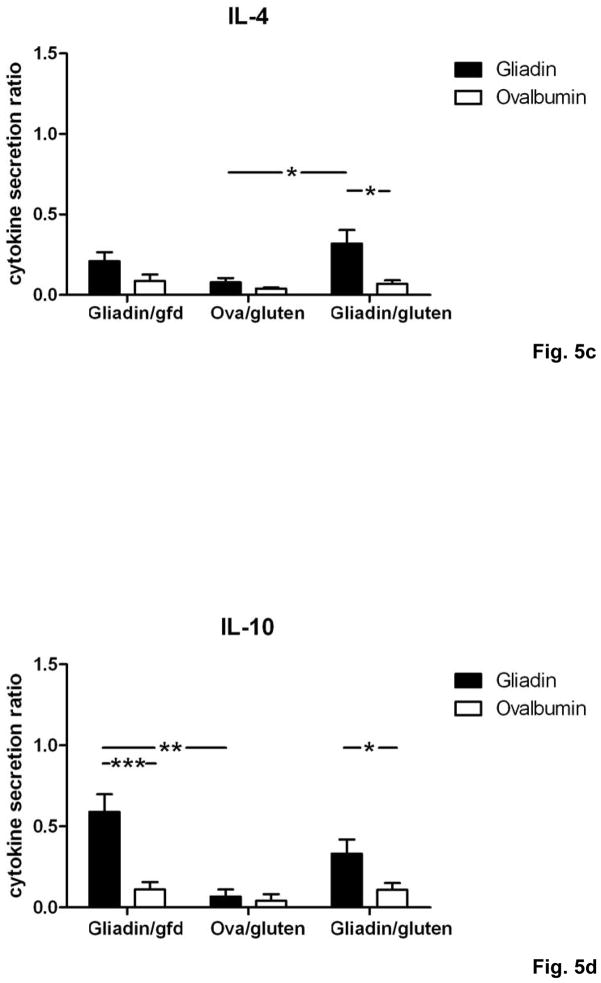
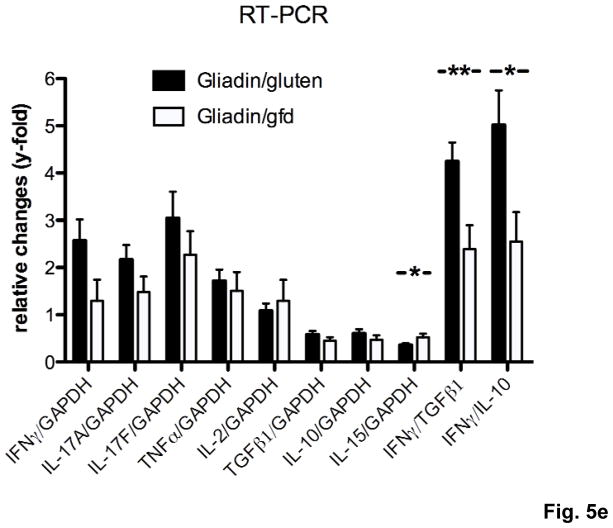
Fig. 5. Th1/Th17 polarization of T cells in Rag1−/− recipients of gliadin-presensitized CD4+CD45RBlowCD25− T cells orally challenged with gluten.
a–d) Splenocytes from individual mice (n=5–12 per group) were restimulated with gliadin or ovalbumin (negative control). Cytokine concentrations in supernatants (ELISA) were refered to internal standard, yielding two ratios for gliadin- and ovalbumin-stimulation. Elevated levels in response to gliadin of a) IFNγ, b) IL-2 and c) IL-4 in the gliadin/gluten vs. the gliadin/gfd and the ovalbumin/gluten groups, and of d) IL-10 in the gliadin/gfd vs. the ovalbumin/gluten and the gliadin/gluten groups (*p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001). e) Increased transcript levels of IFNγ (p=0.06, n.s), IL-17A (p=0.15, n.s.), IL-17F (p=0.33, n.s.) in the duodenum of the gliadin/gluten vs. the gliadin/gfd group, but unchanged levels of TGFβ1 and IL-10 mRNA (RT-PCR). Significant increases for the ratios of IFNγ/TGFβ1 mRNA (**p=0.008) and IFNγ/IL-10 mRNA (*p=0.02). IL-15 mRNA levels were decreased (*p=0.03, n=11–14).