Figure 4.
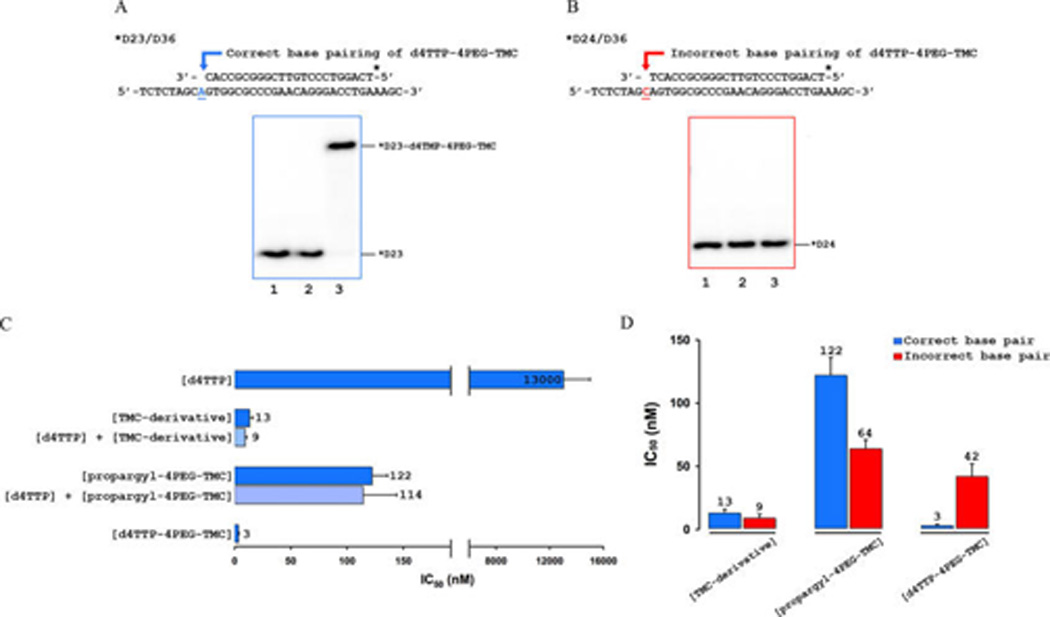
Incorporation and potent HIV-1 RT inhibition of d4TTP-4PEG-TMC is base-specific. (A) Sequence of D23/D36 P/T for correct base pairing used in biochemical assays. d4TTP-4PEG-TMC serves as a substrate for HIV-1 RT-catalyzed polymerization when it is used as a primer for dTTP incorporation. Lane 1 represents the 0 time point, and lane 2 serves as a negative control lacking Mg2+. Lane 3 represents the incorporated bifunctional triphosphate (indicated as *D23-d4TMP-4PEG-TMC) product band by HIV-1 RT. (B) Sequence of D24/D36 P/T for incorrect base pairing used in biochemical assays. d4TTP-4PEG-TMC does not serve as a substrate for HIV-1 RT when it is used as a primer for dGTP incorporation. Lane 1 represents the 0 time point, and lane 2 serves as a negative control lacking Mg2+. Lane 3 shows the lack of an incorporated bifunctional triphosphate product band. (C) Inhibition of dTTP incorporation is shown in bar graphs for d4TTP (13 000 nM), TMC-derivative (13 nM), propargyl-4PEG-TMC (122 nM), and d4TTP-4PEG-TMC (3 nM). Additionally, the calculated IC50 values for 1:1 mixtures of d4TTP/TMC-derivative and d4TTP/propargyl-4PEG-TMC are 9 nM and 114 nM, respectively. IC50 values were determined in triplicate and averaged. (D) Inhibition of dTTP incorporation (correct base pairing) is shown in blue; inhibition of dGTP incorporation (incorrect base pairing) is shown in red. Whereas d4TTP-4PEG-TMC is very potent with proper base pairing (3 nM), its ability to inhibit dGTP incorporation is only slightly more potent (42 nM) than the propargyl-4PEG-TMC (64 nM). Results for TMC-derivative and propargyl-4PEG-TMC are similar for inhibition of dTTP incorporation or dGTP incorporation. Potent RT inhibition of d4TTP-4PEG-TMC is therefore base-specific.
