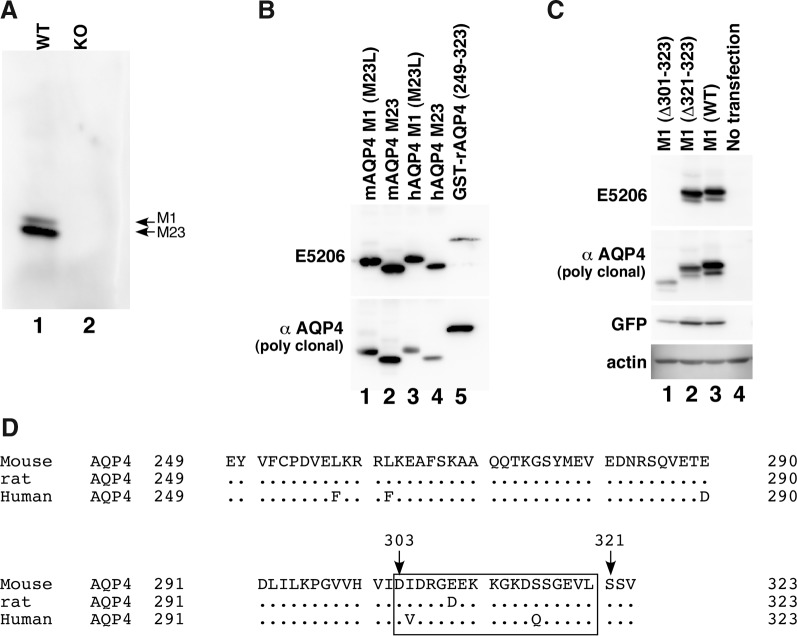
FIG. 1.
Establishment of MAb against the C-terminal domain of AQP4. (A) Western blotting of lysates of a cerebellar membrane fraction derived from either wild-type (lane 1) or AQP4-null (lane 2) mouse using conditioned medium of a hybridoma clone E5206 (1:20). (B) Western blotting of lysates from CHO cells transiently transfected with M23L-mAQP4 M1 (lane 1), mAQP4 M23 (lane 2), M23L-hAQP4 M1 (lane 3), or hAQP4 M23 (lane 4). The GST-fused rAQP4 C-terminal domain, which is the immunogen to raise the polyclonal anti-AQP4 C-terminal domain antibody from Sigma, was also electrophoresed (lane 5). (C) Western blotting of CHO cells transiently transfected with mAQP4 M1 (△301–323, lane 1), mAQP4 M1 (△321–323, lane 2), or wild-type mAQP4 M1 (lane 3). Lysate of CHO cells without transfection was also electrophoresed as a negative control (lane 4). (D) Alignment of protein sequences from Glu249 to Val323 of human, rat, and mouse AQP4, which corresponds to the region used as an immunogen to develop polyclonal rabbit anti-AQP4 C-terminal antibody derived from Sigma. Amino acids conserved among these three species are represented as dots. Amino acids immediately after the truncated site of two deletion mutants are indicated by arrows. The predicted epitope for E5206 is indicated with a box.