FIGURE 4.
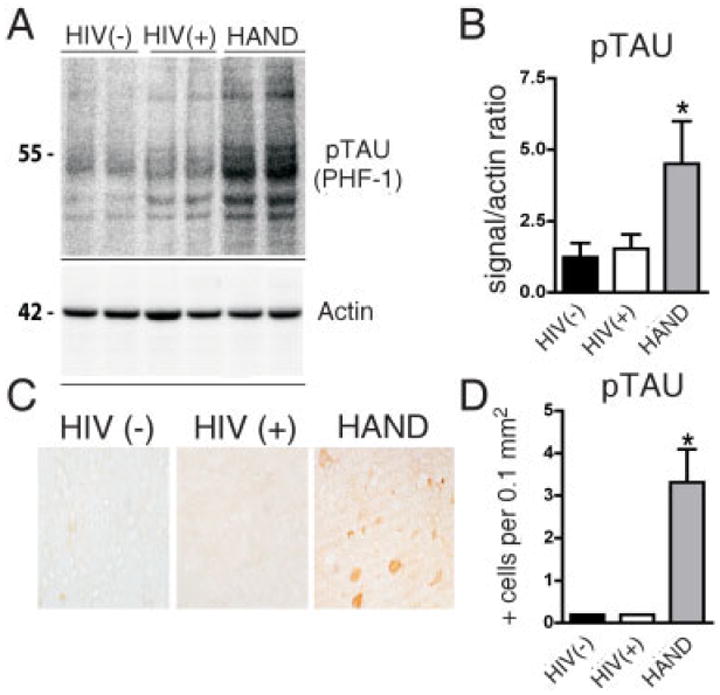
Alterations in phospho-tau levels in basal ganglia from brains of patients with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-associated neurocognitive disorders (HAND). For each group, 5 cases are included. Significantly increased hyperphosphorylated tau (pTAU) was observed in autopsied brain tissue from the basal ganglia (putamen) in all patients with HAND. (A) Western blot analysis of tissue homogenates from the putamen probed with an antibody against pTAU (PHF-1); pTAU is identified as a complex of several bands at an estimated molecular weight of 50–60kDa. (B) Analysis of pixel intensity of the bands using the ImageQuant system. Results are expressed as a ratio of pTAU over actin. (C) Immunohistochemical analysis with antibodies against PHF-1 in the putamen. In HAND brains, occasional positive midsize spine neurons were identified. (D) Image analysis of the numbers of pTAU-positive cells.
