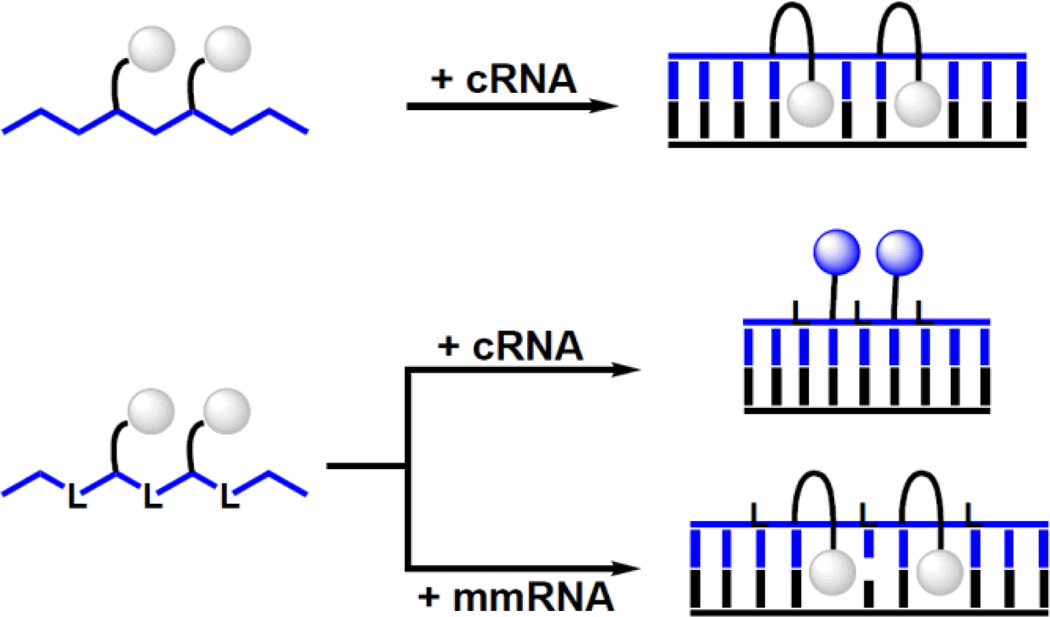
Figure 5.
Principle of SNP-discriminating RNA detection probes reported herein. Upper: Y-modified ‘LNA-free’ reference probes do not result in substantial fluorescence changes upon hybridization with RNA targets due to intercalation of pyrene. Lower: DNA strands with alternating incorporations of LNA and Y monomers result in large hybridization-induced increases in emission with complementary RNA (pyrene in minor groove) but not with mismatched targets (intercalation of pyrene). Droplets represent pyrene moiety of monomer Y. ‘L’, ‘cRNA’ and ‘mmRNA’ denote conventional LNA monomer, complementary RNA, and centrally mismatched RNA target, respectively.