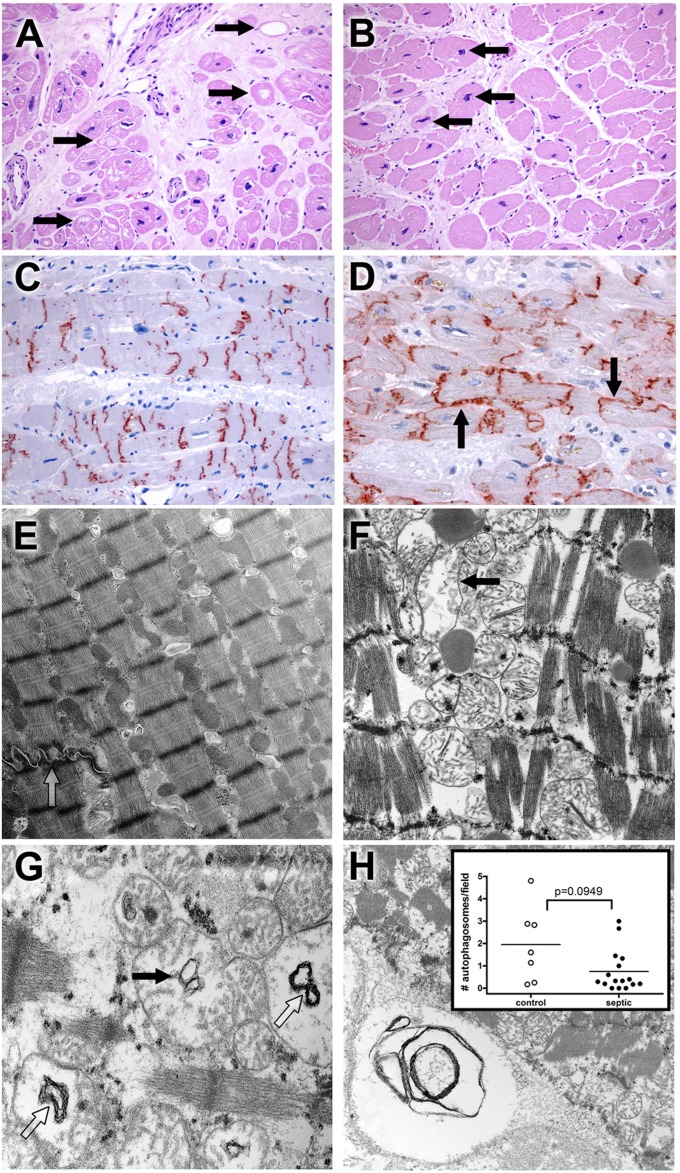
Figure 1.
Light microscopy and ultrastructural findings in heart. (A) Myocytolysis is common in control cardiac myocytes. Hearts were obtained from septic or control patients. Control hearts were failing hearts from patients undergoing heart transplantation or hearts from brain-dead organ donors whose hearts were not acceptable for transplantation (see Methods). Although most myocardial cells were unremarkable in most histologic fields in control and septic samples, large, pale vacuoles in subendocardial myocytes (myocytolysis; arrows), a putative feature of reversible hypoxic injury, were more common in control samples (P < 0.01) (Figure E1). Note also expansion of interstitial fibrous tissue and enlargement of myocyte nuclei (hypertrophy). Original magnification: ×200. (B) Myocyte hypertrophy is common in septic cardiac samples. Although not specific for sepsis, many septic hearts exhibited conspicuous enlargement of myocyte nuclei (hypertrophy; arrows), often in a setting in interstitial fibrosis. Original magnification: ×200. (C) Connexin-43 is present on intercalated discs in control hearts. Strong granular staining of the intercalated discs is seen in this example. Punctate staining of cytoplasm away from the intercalated discs most likely represents intracellular microtubule-mediated transport. Original magnification: ×200. (D) Connexin-43 localizes to lateral cell membranes in some septic specimens. In addition to labeling the intercalated discs, antibodies to connexin-43 also reveal reactivity along lateral myocyte membranes (arrows) in a subset of septic samples. Lateralization of connexin-43 was more common in septic patients (P < 0.05) (Fig. E1). Original magnification: ×400. (E) Electron microscopy of control cardiac muscle. Contractile elements, with distinct Z-bands, are aligned in register. Mitochondria and other organelles occupy space between myofilaments and contractile fibers; most appear normal. Elements of sarcomplasmic reticulum (T tubules) are also evident. A portion of a normal-appearing intercalated disc is present (open arrow). Isolated lipid droplets are present. Original magnification: ×9,730. (F) Electron microscopy of septic cardiac muscle. Contractile elements are in register but are mildly splayed in areas. Mitochondria are relatively normal in appearance but with focal hydropic change (arrow); crista are generally intact. Lipid is present. Original magnification: ×12,800. (G) Mitochondrial abnormalities in sepsis. Hydropic change (edema of the mitochondrial matrix) is associated with cystic alterations of the crista (closed arrow) and collapse into small myelin-like clusters (open arrow). Original magnification: ×18,400. (H) Autophagy in cardiac muscle. Organelle-derived membrane products are packaged in an autophagosome (lower left corner). Original magnification: ×9,730. Insert: Dot plot of average autophagosomes per 3,070× image. The range is wider among control samples, with a higher mean compared with septic samples, but these findings did not reach statistical significance.