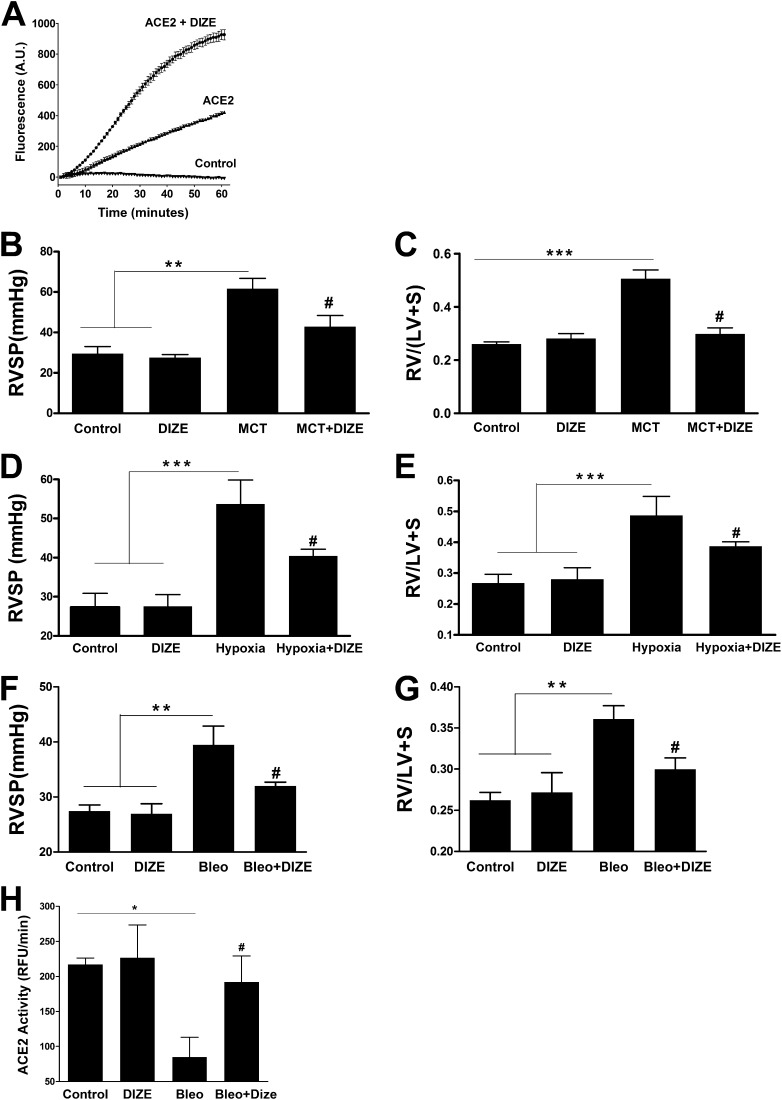
Figure 1.
Diminazene aceturate (DIZE) treatment prevents pulmonary hypertension (PH) and associated cardiac hypertrophy. (A) Coincubation with DIZE (100 μM) increases the enzymatic activity of recombinant human angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) in vitro. (B) Measurement of right ventricular systolic pressure (RVSP) in monocrotaline (MCT)-challenged rats. (C) Right ventricle (RV) hypertrophy reflected by the ratio of RV to left ventricle (LV) plus interventricular septum (S) weight ratio [RV/(LV + S)] in the MCT-induced PH study. (D) RVSP measurement in the hypoxia model of PH. (E) RV/(LV + S) values in hypoxia-exposed rats. (F) Measurement of RVSP in the model of PH secondary to bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis. (G) RV hypertrophy in the bleomycin study. (H) Effect of chronic DIZE treatment on lung ACE2 activity in the bleomycin model of lung injury. Data represent mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001 compared with control rats or rats treated with DIZE group. #P < 0.05 compared with MCT/hypoxia/bleomycin-challenged rats (n = 10 per group for MCT study; n = 6 per group for hypoxia experiments; n = 5 per group for bleomycin study). Bleo = bleomycin.