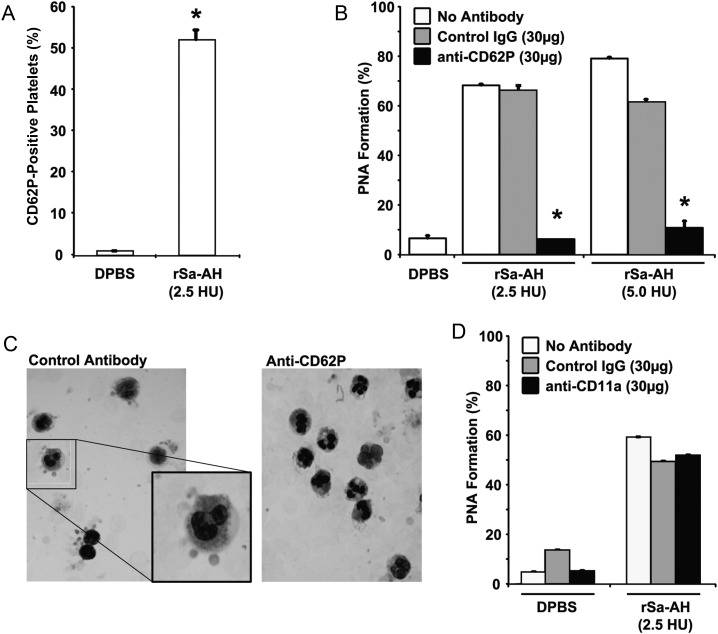
Figure 5.
P-selectin mediates α-hemolysin–mediated platelet-neutrophil aggregate (PNA) formation. A, Recombinant Staphylococcus aureus α-hemolysin (rSa-AH)–induced P-selectin expression on isolated gel-filtered platelets was assessed by flow cytometry, using fluorescein isothiocyanate–CD62P antibody (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Santa Cruz, CA). A total of 2.5 hemolytic units (HU) of rSa-AH equates to 0.06 µg of protein. Data are given as the percentage of platelets expressing CD62P. B, rSa-AH-induced PNA formation was assessed by flow cytometry in the presence of a blocking anti-CD62P antibody, an equal amount of isotype-matched control antibody, or vehicle control (ie, no antibody). C, A Wright's stained cytospin preparation of α-hemolysin–treated whole blood samples from panel B demonstrating a rosette-type pattern of platelet adherence to polymorphonuclear leukocytes in the presence of the control antibody (left; and enlarged inset); rosetting was prevented by anti-CD62P treatment (right). D, rSa-AH–induced PNA formation was assessed in the presence of 30 µg anti-LFA-1 blocking antibody, an isotype-matched control antibody (both from Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Santa Cruz, CA), or vehicle control (ie, no antibody). Data are given as the percentage of dual-positive events and are representative of 2 independent experiments from 2 blood donors. *P < .05, by the Student t test. Abbreviations: DPBS, Dulbecco's phosphate-buffered saline; IgG, immunoglobulin.