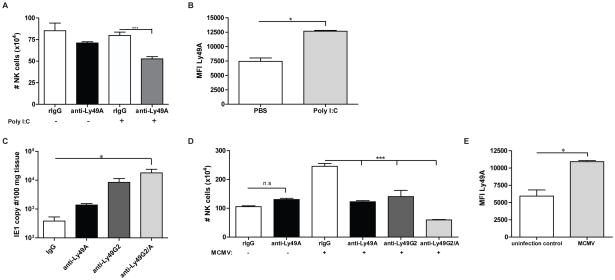
Figure 6. Increased Ly49A expression in H2d strains allows for efficient NK cell depletion by anti-Ly49A.
B10.D2 mice were treated with control rIgG or anti-Ly49A (clone YE1/32) with poly(I:C) or PBS administration one day prior to harvest. (A) Total number of NK cells is shown. (B) Ly49A MFI was calculated on gated NK cells after PBS or poly(I:C) treatment. (C–E) B10.D2 mice were treated with control rIgG, anti-NK1.1, anti-Ly49A and/or anti-Ly49G2 two days prior infection with MCMV 5×104 PFU. (C) Seven days post-infection liver MCMV viral loads were measured by PCR. (D) Total numbers of NK cells were calculated from the spleen. (E) The MFI for Ly49A+ NK cells is shown for non-MCMV and MCMV infected mice. Data are representative of two experiments with 3–4 mice per group (mean ± SEM). Two-tailed Student’s t-test or One-way Anova was used to assess significance when appropriate (*p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001; n.s: not significant).