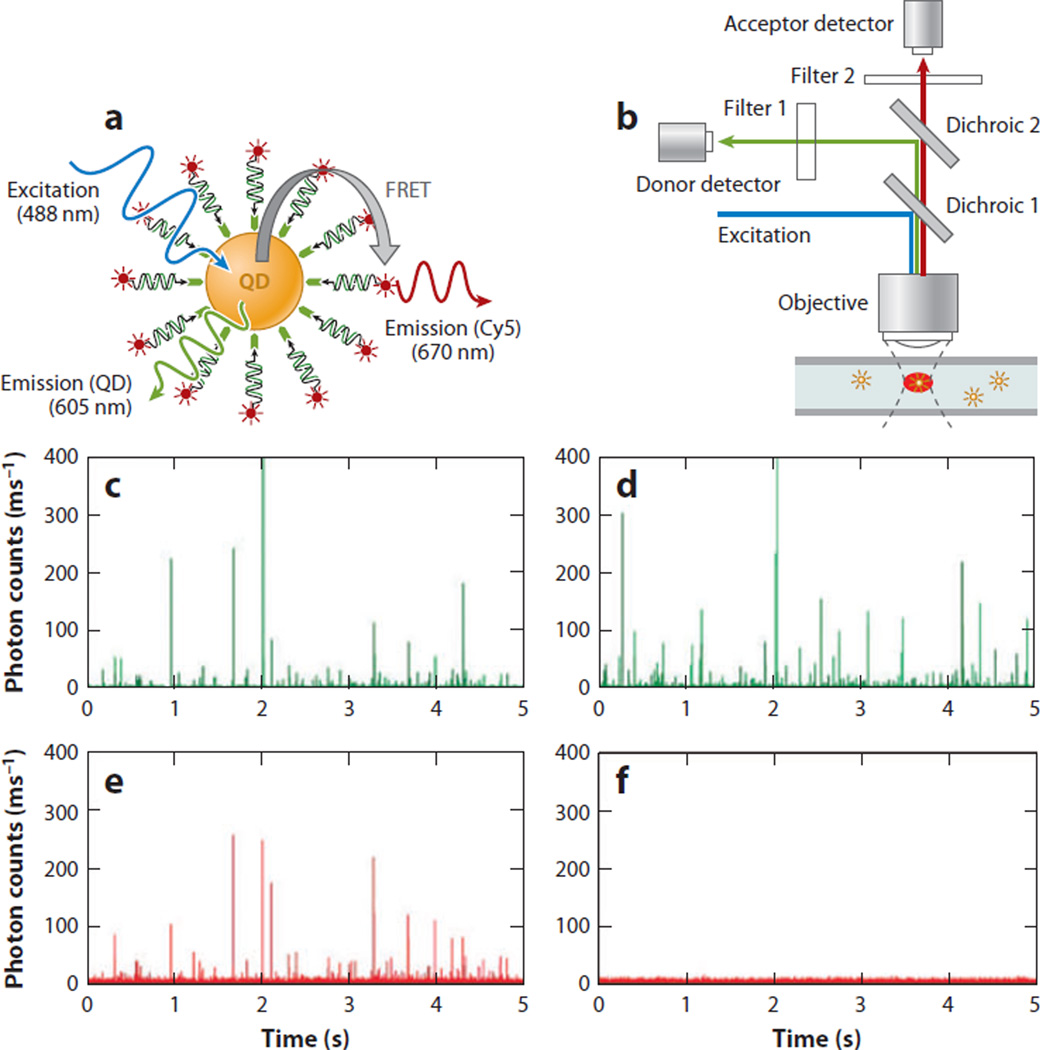
Figure 8.
Quantum dot (QD) nanosensor for the detection of DNA. (a) A QD nanosensor with bioconjugated capture sequences, bound to target DNA and a dye-conjugated reporter sequence in a sandwich assay. The reporter sequence brings the dye into close proximity to the nanocrystal and is excited by fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) between the dye acceptor (Cy5) and the QD donor. (b) Experimental flow setup for the detection of QDs and dye signal. In the presence of the target sequence, coincident fluorescence signals are measured in both the donor (c) and acceptor (e) detectors. In the absence of the target sequence, signal is detected only from the QD donor (d) and is not observed on the acceptor detector (f). Adapted from Reference 102.