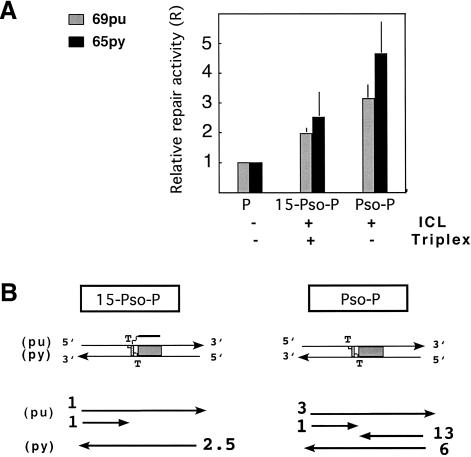
Figure 3.
Quantification of the abundance of the neo-synthesized fragments due to repair processing of the different cross-linked DNA substrates. (A) Relative repair activities (R) of full-length repair products: purine (light grey) and pyrimidine (dark grey) strands were reported for each template (as indicated). They were obtained after dividing the relative abundance of neo-synthesized products (obtained by nucleotide incorporation) by their relative abundance in the initial mixture (obtained by kinase labelling) (average of three experiments; see details in Materials and Methods). (B) Schematic representation of the various neo-synthesis fragments obtained in vitro for the two different psoralen cross-linked substrates used in the present work. Purine and pyrimidine full-length or futile repair fragments are represented with their associated stoichiometries, calculated on the basis of fragment signal intensities and cytosine contents (mean from four experiments). For each of the full-length fragments, the background synthesis, estimated from (A) by comparison of the undamaged substrate (P) with the damaged ones (Pso-P and 15-Pso-P), was deduced in order to obtain the level of repair-induced synthesis.