Figure 1.
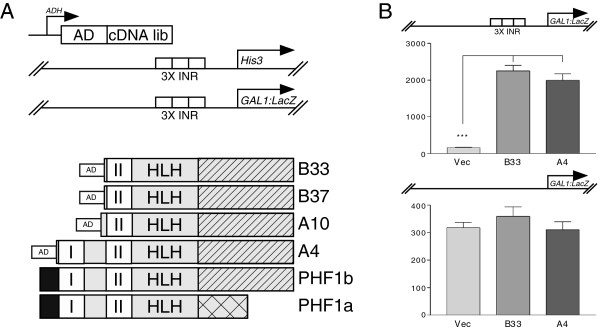
Results of a yeast one-hybrid assay using expressed human brain cDNAs and β1-INR sequences. A) The NLY2 yeast strain was transformed to contain two integrated reporters (His3 and LacZ) (top panel) under the control of three tandem β1-INRs. This strain was used to screen a yeast expression library containing cDNAs derived from human adult or fetal brains. cDNAs were expressed from a yeast 2 micron based multi-copy plasmid with expression controlled by the ADH promoter. The libraries of expressed proteins contain a GAL4 activation domain (AD) fused to each cDNA in frame to facilitate one-hybrid screening in yeast. Transformed yeast colonies were screened for their ability to grow on selective solid media containing 10 mM 3-aminotriazole and lacking histidine. To confirm clone selection, expression of β-galactosidase was measured by plating yeast colonies on plates containing chromogenic dye (X-gal). Purified clones are shown in relation to the wild type and full length PHF1b (human Polycomblike protein) and PHF1a sequence. Two plant homeodomain (PHD) fingers are shown (I or II) with white boxes. Black box represents the amino terminus. Different carboxyl termini that result from alternative splicing are shown with hatched (PHF1b) and cross-hatched bars (PHF1a). A putative helix-loop-helix forming sequence is depicted by “HLH”. B) Screened candidates require INR sequence for reporter gene activation. Top panel shows candidates A4 and B33 activates β-galactosidase reporter gene only when reporter promoter contains the INR sequence. A reporter without INR sequence (bottom panel) shows no activity from the candidates in comparison to the vector plasmid. Results are expressed as mean values ± SEM.
