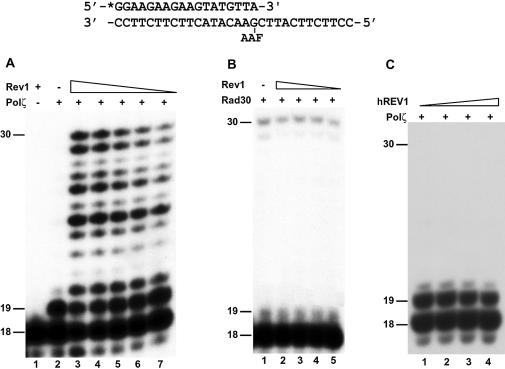
Figure 5.
Effect of Rev1 protein on Polζ-catalyzed extension synthesis from opposite the AAF-dG adduct. An 18mer 32P-labeled primer was annealed to a damaged 30mer template with the primer 3′ A opposite the AAF-dG adduct as shown on the top. (A) DNA polymerase assays were performed with 16 ng (79 fmol) of yeast Polζ in the absence (lane 2) or presence (lanes 3–7) of 63 ng (562 fmol), 32 ng (286 fmol), 21 ng (188 fmol), 15 ng (134 fmol) and 10 ng (89 fmol), respectively, of purified yeast Rev1 protein. Lane 1, DNA polymerase assay with 63 ng of Rev1 alone. (B) DNA polymerase assays were performed with 12 ng (169 fmol) of yeast Polη in the absence (lane 1) or presence (lanes 2–5) of 26 (232 fmol), 13 (116 fmol), 7 (63 fmol) and 3 ng (27 fmol), respectively, of purified yeast Rev1 protein. (C) DNA polymerase assays were performed with 21 ng (104 fmol) of yeast Polζ in the presence of 13 (94 fmol, lane 1), 26 (188 fmol, lane 2), 39 (283 fmol, lane 3) and 52 ng (377 fmol, lane 4) of purified human REV1 protein. DNA size markers in nucleotides are indicated on the left.