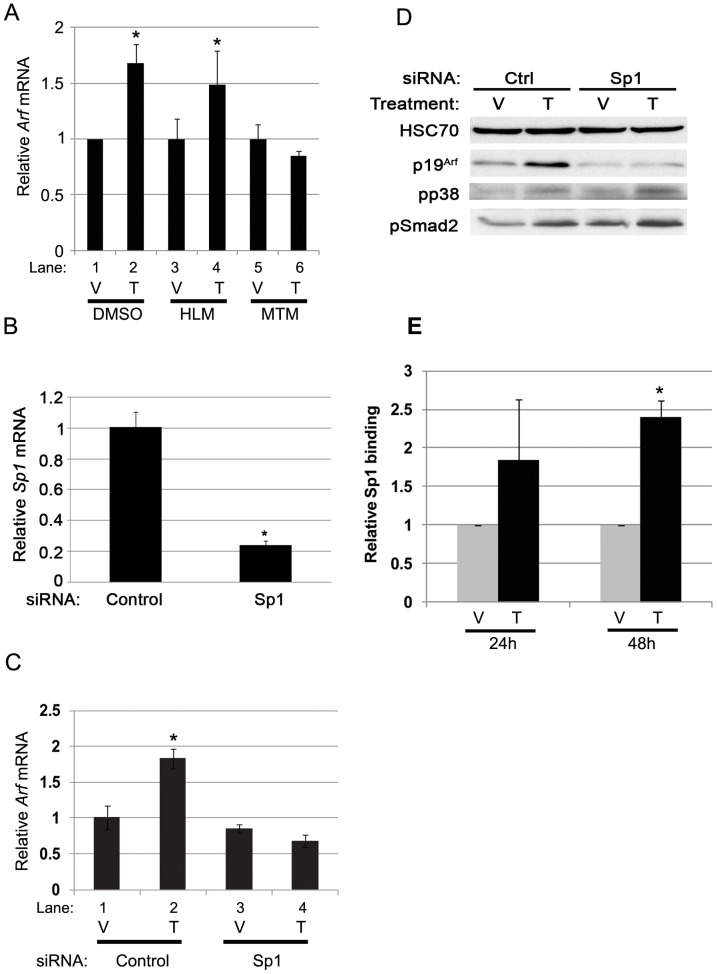
Figure 5. Inhibition or knockdown of Sp1 blocks Arf mRNA induced by Tgfβ.
(A) qRT-PCR analysis using total RNA isolated from WT MEFs treated with Sp1 inhibitor, mithramycin A (MTM), E2F inhibitor, HLM006474 (HLM) and control DMSO, following 48 hour exposure to Tgfβ (T) or vehicle (V). The significant changes between Tgfβ treatment and vehicle treatment is marked as * (p<0.05). (B) qRT-PCR analysis of Sp1 using total RNA isolated from WT MEFs treated with either siRNA control (Scram), or siRNA targeting mouse Sp1 as indicated for 48 hours. *, p<0.05. (C) qRT-PCR analysis using total RNA isolated from WT MEFs treated with Tgfβ (T) or vehicle (V) for 48 hours following 24 hours transfection with either siRNA control (Scram), or siRNA targeting mouse Sp1 as indicated. Sp1 knockdown significantly dampens the induction of Arf mRNA by Tgfβ (*, p<0.05). (D) Representative western blot for the indicated proteins using lysates from wild type MEFs treated with Tgfβ (T) or vehicle (V) for 48 hours following 24 hours transfection with either siRNA control (Scram), or siRNA targeting mouse Sp1 as indicated. (E) Tgfβ promotes Sp1 binding to the Arf locus in MEFs. Quantitative analysis of representative ChIP assays using wild type MEFs exposed to vehicle (V) or Tgfβ (T) for 24 hours or 48 hours. ChIP assay was carried out using antibodies specific to Sp1 and IgG as control. Immunoprecipitated DNA and input DNA were amplified with primers for proximal region of Arf promoter. *, p<0.05 for Tgfβ versus corresponding vehicle.