Figure 4. Identification and characterization of potential adaptive mutations.
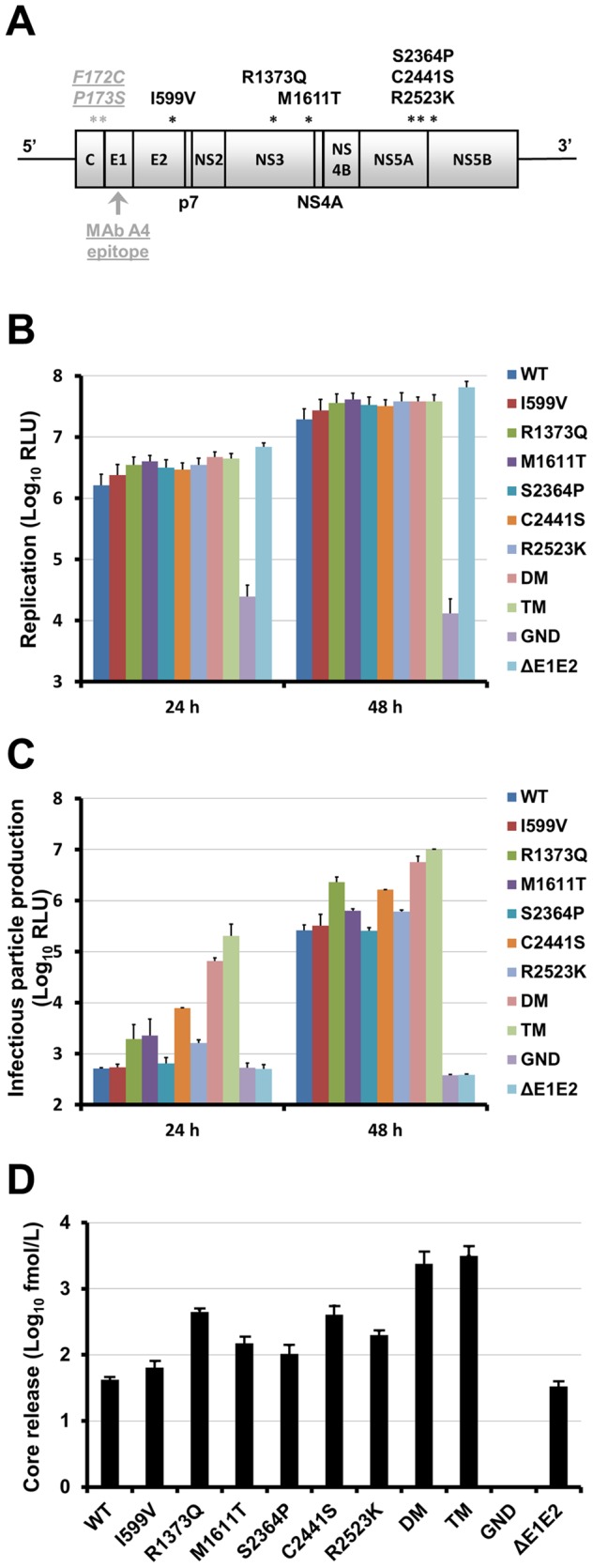
(A) Positions of conserved mutations found in the adapted virus on JFH1 open reading frame schematic diagram. The originally introduced amino acid changes F172C and P173S in Core and A4 MAb epitope in E1 are indicated in underlined gray type. Mutations identified at the end of the selection are indicated in black type. (B, C, D) Effect of the potential adaptive mutations on viral genome replication, infectious virus production and HCVcc assembly/secretion. HuH-7-RFP-NLS-IPS cells were transfected with JFH1-CS-A4-RLuc RNA (WT) or mutated HCV genomes (I599V, R1373Q, M1611T, S2364P, C2441S, R2523K, R1373Q/C2441S (DM for double mutant) or R1373Q/M1611T/C2441S (TM for triple mutant)). An assembly-deficient virus (ΔE1E2) and a replication-defective virus (GND) were used as controls. (B) Replication was assessed at 4, 24 and 48 h by measuring Renilla Luciferase activities in transfected cells. Results are expressed as relative light units (RLU) normalized at 4 h and are reported as the means ± S.D. of two independent experiments. (C) The supernatant of transfected cells were recovered at 24 and 48 h and incubated for 3 h with naive HuH-7-RFP-NLS-IPS cells. Luciferase assays were performed on infected cells at 72 h post-infection. Results are expressed as RLU and are reported as the means ± S.D. of two independent experiments. (D) HCV core release was quantified in the supernatants recovered 48 h post-transfection. Results are expressed as Core fmol/L and are reported as the means ± S.D. of two independent experiments.
