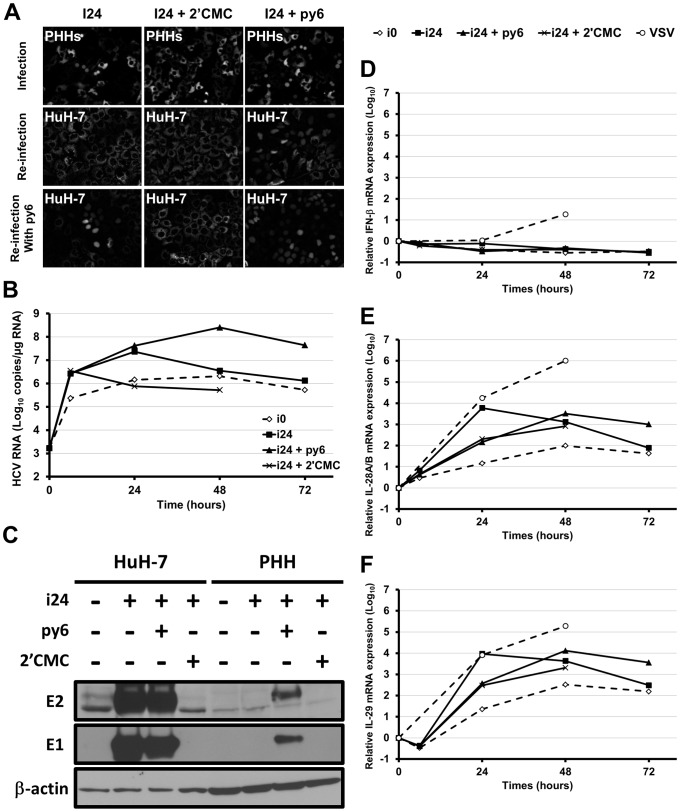
Figure 5. Infection of PHHs with cell culture adapted HCV.
PHHs from one representative donor were inoculated for 6 h with non-adapted HCV (i0; MOI = 0.01 HuH-7 infectious units per cell) or i24 (MOI = 1000 HuH-7 infectious units per cell), in the presence or absence of 2′CMC (10 µM) or py6 (500 nM). After inoculation, cells were washed three times with PBS and new media containing the drugs were added and replaced every day. (A) Infection of PHHs that had previously been transduced with lentivirus expressing RFP-NLS-IPS, was visualized 48 h post-infection by translocation of the cleavage product RFP-NLS to the nucleus (“Infection” panel). The supernatants of inoculated cells were recovered 48 h post-infection, centrifuged and used to inoculate naive HuH-7-RFP-NLS-IPS in the absence or presence of py6 (“Re-infection” and “Re-infection with py6” panels, respectively) to check the production of progeny virus. Infected HuH-7 cells were visualized 48 h post-infection. (B) Intracellular HCV RNA was quantified by RT-qPCR, after inoculation of non-transduced PHHs. Results are expressed as means ± S.D. of duplicates. (C) Expression of the viral proteins E1 and E2 was analyzed 48 h post-infection in cell lysates by Western blotting using specific MAbs (A4 [anti-E1], 3/11 [anti-E2], and C4 [anti-β-actin]). HuH-7 cells infected in the same conditions were used as control. (D, E, F) IFN-β, IL-28A/B and IL-29 expression in infected PHHs was determined in duplicate by RT-qPCR. The results are normalized to GAPDH endogenous control and presented as fold-increase over pre-infection levels, using the ΔΔCt method.