Figure 1.
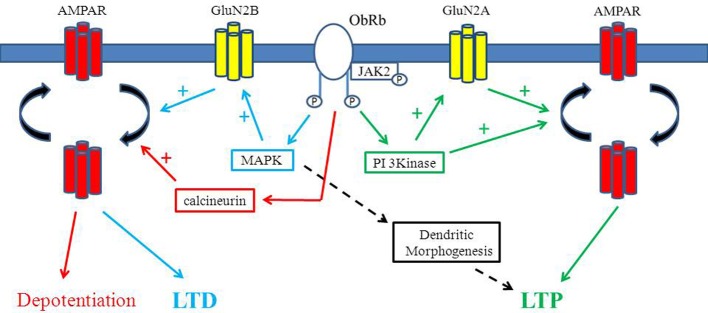
Divergent effects of leptin on hippocampal synaptic function. Schematic representation of the key signaling pathways that contributes to the diverse effects of leptin in the hippocampus. Activation of leptin receptors triggers PI 3-kinase stimulation which results in AMPA receptor exocytosis and a sustained increased in synaptic efficacy (leptin-induced LTP). Leptin driven stimulation of PI 3-kinase also enhances GluN2A activity which in turn promotes AMPA receptor delivery to synapses and subsequent LTP at adult hippocampal CA1 synapses. In contrast, at early stages of postnatal development, leptin dependent activation of the ERK (MAPK) signaling cascade facilitates GluN2B-mediated responses resulting in either persistent (LTD) or transient depressions in excitatory synaptic transmission. Leptin is also capable of depotentiating hippocampal synapses via a process involving the activation of calcineurin and subsequent endocytosis of GluA2-lacking AMPA receptors. Rapid alterations in dendritic morphology are also evoked by leptin that are mediated by the MAPK (ERK) signaling cascade.
