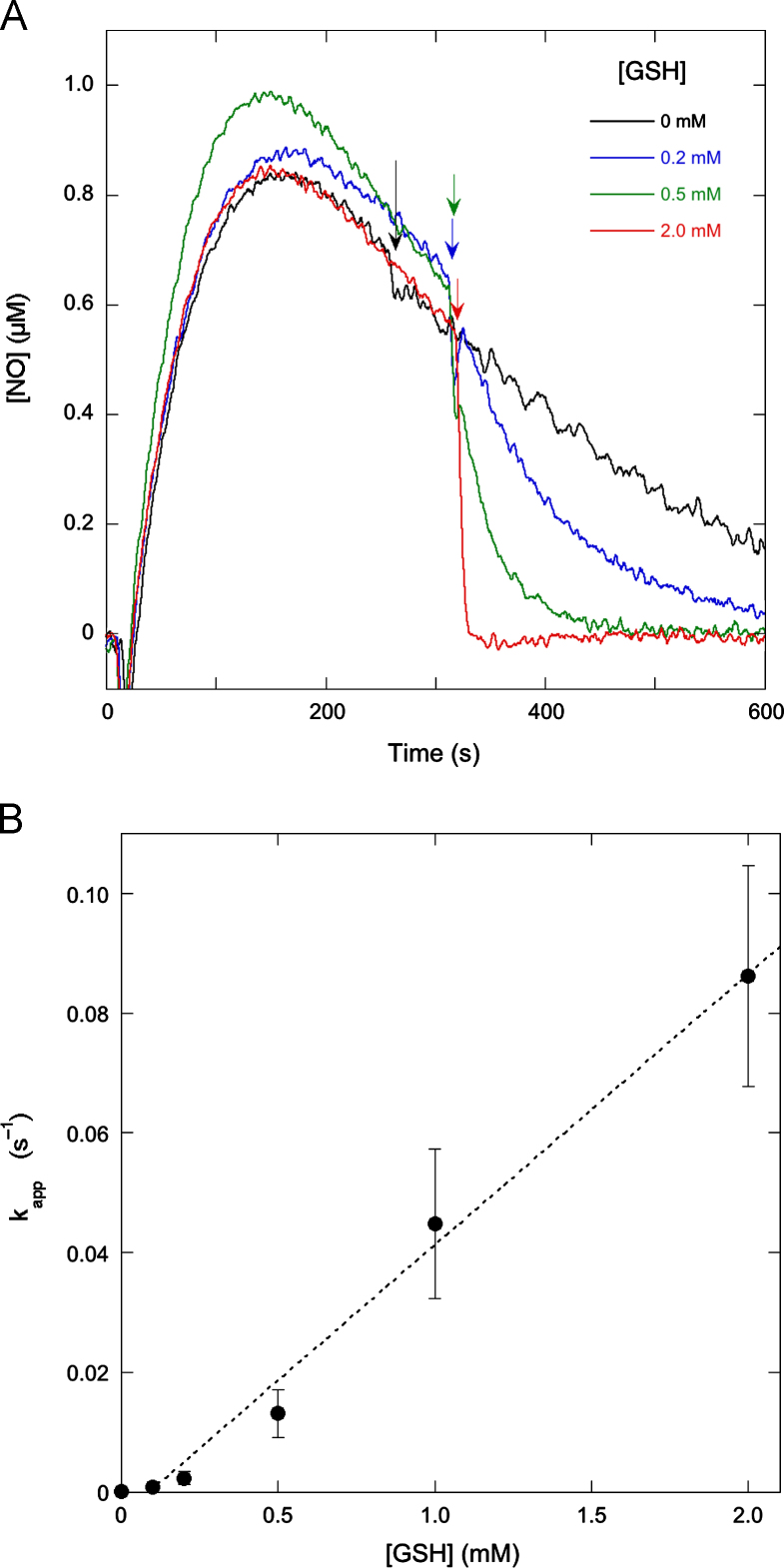
Fig. 9.
Effect of the GSH concentration on the NO decay rate. (A) The effect of the addition of various concentrations of GSH on the NO release curve. NO released from 1 µM DEA/NO in the absence of GSH was measured as for Fig. 1. At the time indicated by the arrows GSH (0.2, 0.5, or 2.0 mM as indicated) was added to the reaction mixture. (B) The apparent pseudo-first-order rate constant as a function of the GSH concentration. Pseudo-first-order rate constants were obtained by dividing the GSH-induced NO decay rate, i.e., the difference between the rates before and after GSH addition, by the NO concentration at the time of GSH addition (which varied between the individual experiments). The dotted line is the best linear fit. An apparent second-order rate constant of 34±6 M−1 s−1 was calculated as the average of the quotients of the apparent pseudo-first-order rate constant and the GSH concentration for all experiments. Experimental conditions: 1 µM DEA/NO, GSH as indicated, 4 mM CuSO4, 1000 U/ml SOD, 0.1 mM DTPA, 5 mM MgCl2, and 50 mM TEA (pH 7.4) in 0.5 ml at 37 °C.