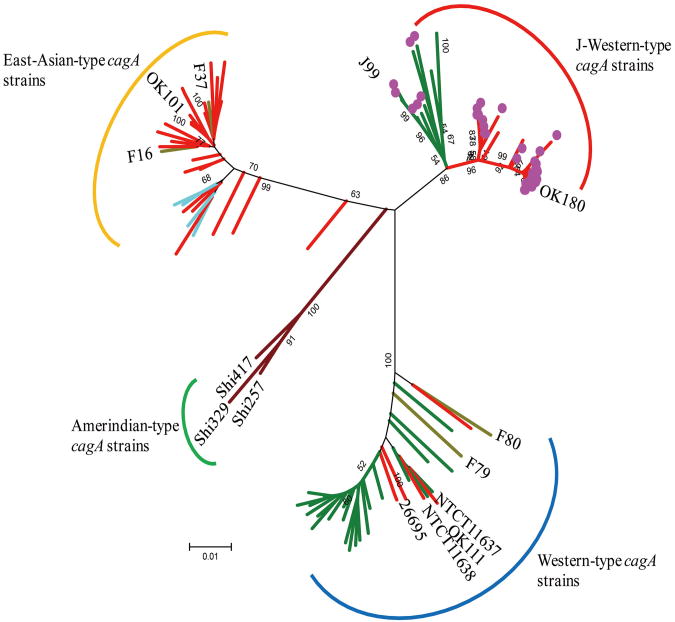
Fig.1. Phylogenetic tree constructed on the basis of the cagA sequence.
Pylogenetic tree was constructed by using cagA sequence (about 1000 bp) including 12-bp insertion. cagA sequences of 14 strains (J99, 26695, NCTC11637, NCTC11638, F16, F37, F79, F80, OK101, OK111, OK180, Shi257, Shi329, and Shi417) were obtained from Genbank. Neighbor joining tree was constructed in MEGA 5.0 using bootstrapping at 3,000 bootstrap trials and through Kimura-2 parameters. Scale bars indicate the calculated distance. Red branch show the strains from Okinawa. Dark yellow branch show the strains from Fukui. Blue branch show the strains from Western countries. Light blue branch show the strains from Vietnamese who live in the U.S. Brown branch show the strains from Amerindian. Strains with 12-bp insertion were indicated as purple circle. Each cagA type was determined based on the 5′ region of cagA sequence (i.e., 2 East-Asian-type cagA strains based on the 3′ region of cagA sequence with 12-bp insertion located in the same cluster with other strains with 12-bp insertion, suggesting that 2 strains have J-Western-type cagA structure in the 5′ region of cagA, whereas East-Asian-type cagA structure in the 3′ region of cagA).