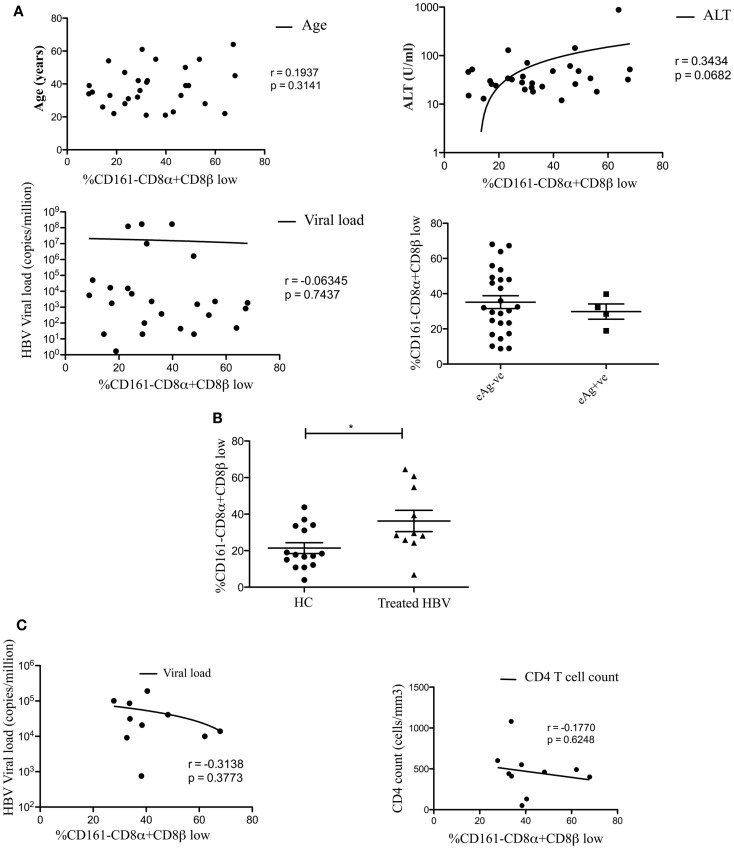
Figure 2.
CD161−CD8α+CD8β− T cell populations develop independent of clinical status in chronic HBV and HIV-1 infections. (A) Analysis of the correlation between the size of the CD161−CD8α+CD8βlow T cell population and patient age/viral load (Pearson) and comparison of the size of the CD161−CD8α+CD8βlow population, as a proportion of the CD161−CD8α+ population, between patients e-antigen positive and e-antigen negative patients (Mann Whitney test) in chronic HBV infection. (B) Analysis of the % of CD161−CD8α+CD8βlow T cells as a proportion of the CD161−CD8α+ population in patients with treated with chronic HBV compared to HC (*p < 0.05, unpaired t test). (C) Correlative analysis between the size of the CD161−CD8α+CD8βlow T cell population as a proportion of the CD161−CD8α+ population and viral load/CD4 count in HIV-1 infection (Pearson).