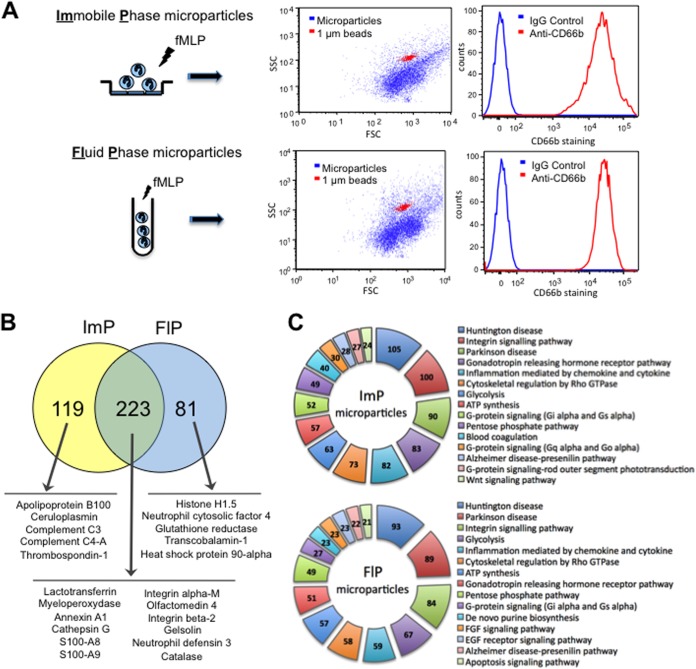
Fig. 1.
Differential stimulation of neutrophils yields microparticles with a distinct proteome. A, The physical properties of microparticles - obtained from neutrophils after stimulation in fluid-phase (FlP; in suspension) or immobilized-phase (ImP; post adhesion to a HUVEC monolayer - were assessed employing the forward and side scatter parameters on the dot-plot generated by flow-cytometric analysis. The origin from the neutrophil was ascertained by staining the microparticles by anti-CD66b staining. B, Venn diagrams representing the proteomic content identified in each of the neutrophil microparticle subsets as determined using tandem LC-MS-MS. C, Ingenuity Pathway Analysis software was used to highlight the top 15 functions of the various proteins expressed in the distinct microparticle subsets as illustrated. In all cases results are representative of four distinct analyses.