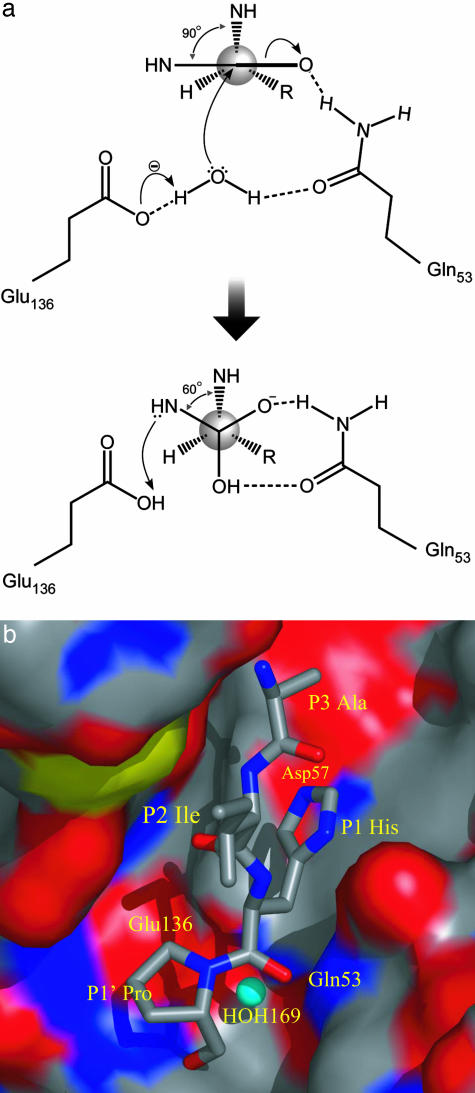
Fig. 6.
(a) The proposed catalytic mechanism of SCP-B. The water molecule hydrogen-bonded to both Glu-136 and Gln-53 is the nucleophile. The general base is the carboxylate of Glu-136. The side-chain amide of Gln-53 assists in the nucleophilic attack and stabilizes the tetrahedral intermediate by hydrogen bonding. (b) A model of a substrate Ala-Ile-His-Pro bound in a productive mode in the active site of SCP-B. The nucleophilic attack by the OH- ion (blue sphere) is on the si-face of the scissile peptide. The surface of SCP-B is represented and colored according to the underlying atoms (slate, carbon; blue, nitrogen; red, oxygen).