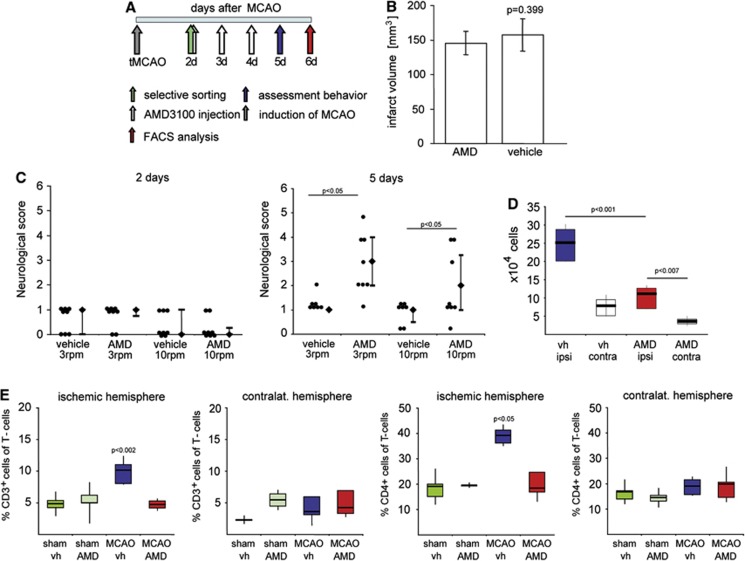
Figure 3.
Treatment with the specific CXCR4 antagonist AMD3100 suppressed immune cell invasion in the ischemic hemisphere and improved functional recovery after experimental stroke. (A) Experimental design. Male Wistar rats were subjected to transient occlusion of the middle cerebral artery (tMCAO). Two days later, neurologic deficit was evaluated by the rotating pole test and only animals with a test score of 2 or lower were randomized into treatment groups receiving either AMD3100 (0.5 mg/kg intraperitoneal twice daily) or saline (vehicle (vh), intraperitoneal twice daily) for 3 consecutive days. On day 5 after tMCAO, neurologic score was evaluated, and on day 6, brains were analyzed for the invasion of immune cells. (B) Infarct volumes of vehicle (n=5) and AMD3100-treated rats (n=5) at day 6 after tMCAO. Values are presented as mean±s.d., Student's t-test. (C) Rat sensorimotor score obtained on the rotating pole (at 3 and 10 rotations per minute to the right) 2 and 5 days after tMCAO after treatment with AMD3100 (n=8) or saline (n=8). Difference in functional recovery was significant between the two treatments (Mann–Whitney). The values are presented as the median with the 25th to75th percentiles (bars), individual scores are presented to the left. (D) Number of immune cells in the ischemic (ipsi) and contralateral (contra) hemisphere after treatment with AMD3100 (AMD) or vehicle after tMCAO. Results are presented as the median with the 25th to75th percentiles (bars) and the 95% confidence interval (CI), one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA), Bonferroni correction. (E) Effect of AMD3100 treatment on CD3+ and CD3+/CD4+ cells in the injured and contralateral hemisphere 6 days after tMCAO or sham operation. The values are presented as the median with the 25th to 75th percentiles and 95% CI, one-way ANOVA, Bonferroni correction versus MCAO AMD. FACS, fluorescence-activated cell sorting.