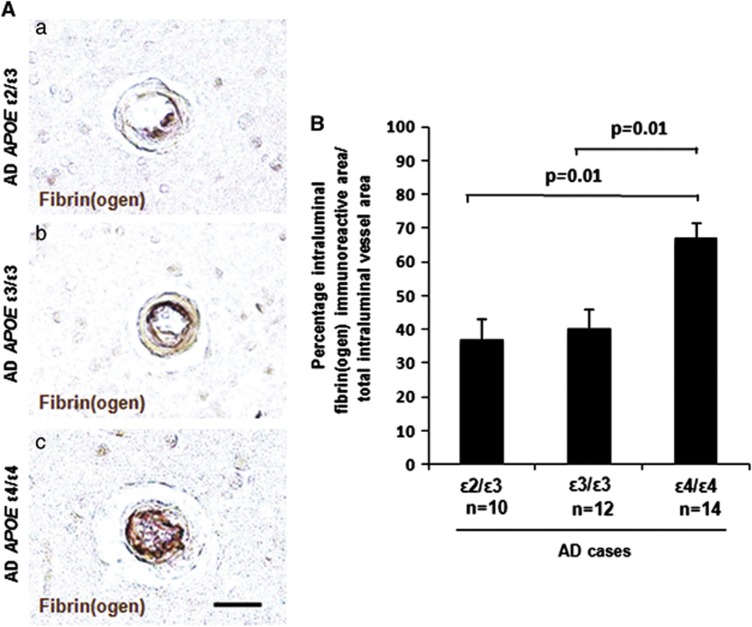
Figure 4.
Increased intraluminal deposition of fibrin(ogen) in cerebral amyloid angiopathy (CAA)-positive vessels in Alzheimer's disease (AD) apolipoprotein E (APOE) ɛ4/ɛ4 cases. Immunostaining of fibrin(ogen) and CAA was performed on cortical sections from AD brains, and the percentage of intraluminal vessel area staining positive for fibrin(ogen) relative to the total intraluminal vessel area was quantified. (A) Representative images of intraluminal fibrin(ogen) deposition in AD APOE ɛ2/ɛ3 (a), AD APOE ɛ3/ɛ3 (b), and AD APOE ɛ4/ɛ4 (c) cases. Scale bar, 20 μm. (B) A significantly higher percentage of the total intraluminal area was immunoreactive for fibrin(ogen) in AD APOE ɛ4/ɛ4 cases compared with AD APOE ɛ3/ɛ3 (P=0.01) or ɛ2/ɛ3 (P=0.01) cases. Differences between groups were evaluated by one-way analysis of variance and Tukey's post-hoc test. Values are presented as mean±s.e.m.