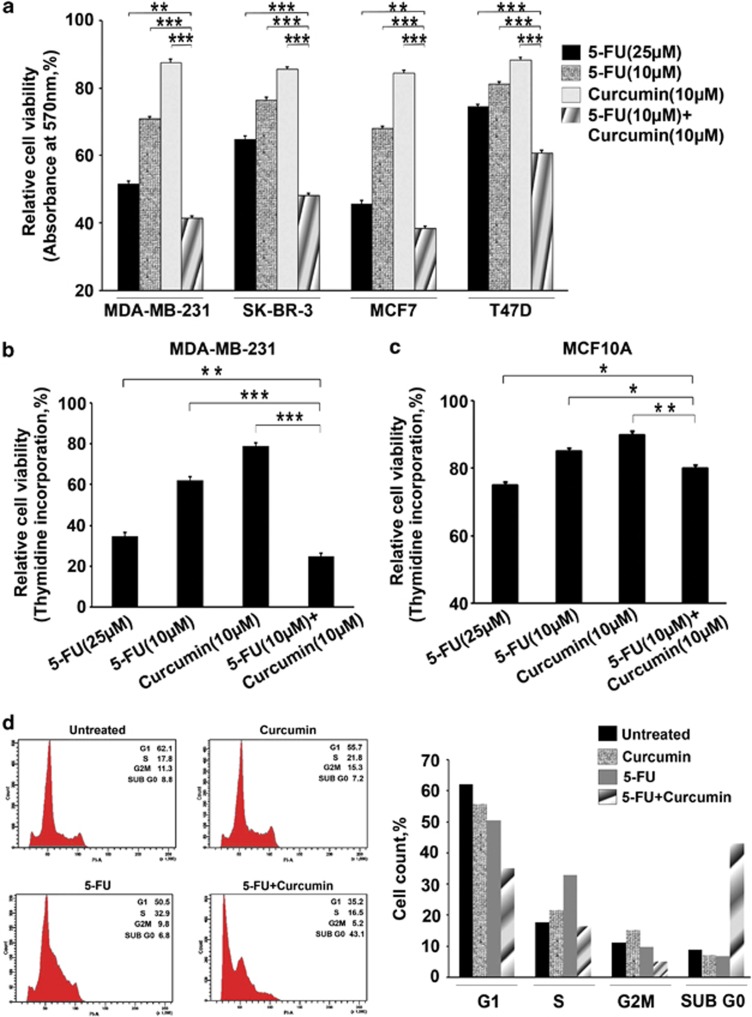
Figure 1.
Curcumin sensitizes breast cancer cells to 5-FU-induced apoptosis, while normal breast cells are unaffected. (a) Effect of 5-FU and curcumin, alone or in combination, on various breast cancer cells. A total of 5000 cells in triplicates were exposed to the indicated concentrations of the drugs for 48 h and subjected to 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay. Relative cell viability was determined as percentage absorbance over untreated control. Data represent three independent sets of experiments and results are shown as the mean±S.D. *** and ** represents P-values ⩽0.0001 and ⩽0.001 respectively. (b) Effect of 5-FU and curcumin, alone or in combination, on MDA-MB-231 cells. A total of 5000 cells in triplicates were exposed to the indicated concentrations of the drugs for 24 h and subjected to [3H]thymidine incorporation assay. Relative cell viability was determined as percentage thymidine incorporation over untreated control. The data represent three independent experiments. *** and ** represents P-values ⩽0.0001 and ⩽0.001 respectively. (c) Effect of 5-FU and curcumin, alone or in combination, on normal immortalized breast epithelial cells using [3H]thymidine incorporation assay as described above. ** and * represents P-values ⩽0.001, ⩽0.05 respectively. (d) Effect of 5-FU and curcumin, alone or in combination, on cell cycle. Cells were harvested after 48 h of drug treatment, fixed in alcohol, stained with propidium iodide and assayed for DNA content by flow cytometry. Representative histograms on the right-hand panel indicate the percentages of cells in G1, S, G2/M and sub-G0 phases of the cell cycle. The percentage of cells with sub-G0 DNA content was taken as a measure of the apoptotic cell population. The data provided are representatives of three independent experiments