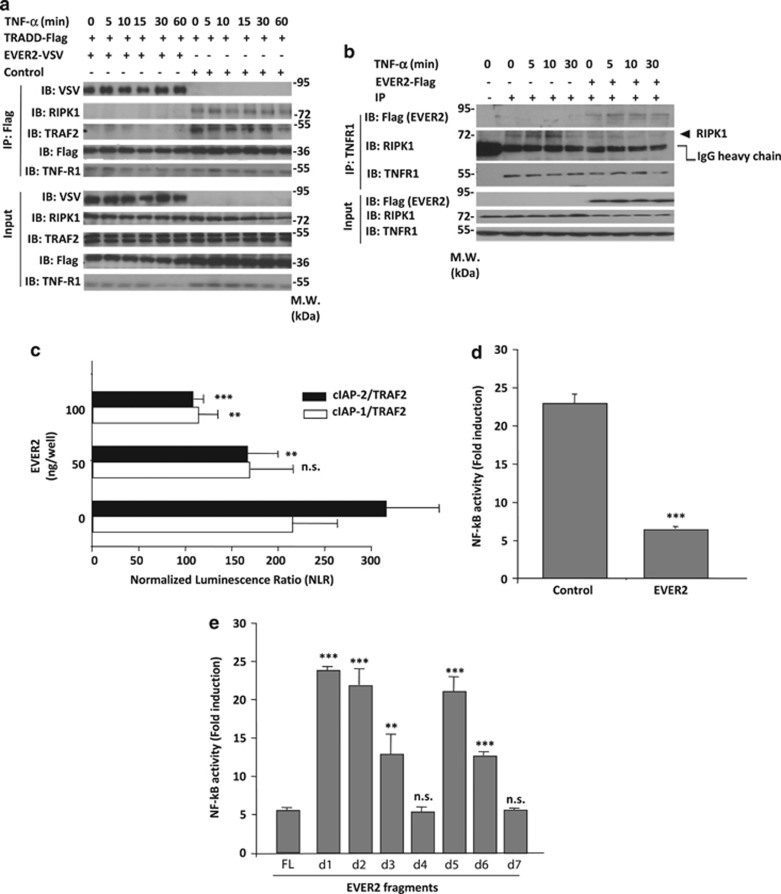
Figure 5.
EVER2 interaction with TRADD impairs TRADD/RIPK1/TRAF2/cIAPs complex I formation and TNF-α-induced NF-κB activation. (a) TRADD/RIPK1/TRAF2 complex I formation is impaired in EVER2-expressing cells. Cells were cotransfected with EVER2–VSV or empty vector and TRADD–Flag constructs. Cells were stimulated with TNF-α (10 ng/ml) for various time periods, lysed and subjected to IP with anti-Flag-specific antibody. IB was performed with indicated antibodies. (b) EVER2 overexpression impairs RIPK1 recruitment to TNFR-1 complex I. Cells were transfected with empty or EVER2 expression vector and stimulated with TNF-α (10 ng/ml) for various time periods. Cells were lysed and subjected to IP with anti-TNFR-1-specific antibody or non specific isotype IgG (shown as −). IB was performed with indicated antibodies. (c) TRAF2/cIAP-1 and TRAF2/cIAP-2 interaction in the presence or absence of EVER2, as assessed by HT–GPCA. Cells were transfected with TRAF2–Gluc1 and cIAP-1–Gluc2 or cIAP-2–Gluc2 constructs, in the absence or presence of various amounts of EVER2–Flag. Student's t-test comparing TRAF2–cIAPs interaction in the presence (50–100 ng) and absence of EVER2: ***P<0.001; **P<0.005. (d) Measurement of TNF-α-induced NF-κB activation in the NF-κB plasmid reporter assay. Cells were cotransfected with NF-κB plasmid reporter and EVER2–Flag or empty vector as a control. Cells were stimulated with TNF-α (10 ng/ml) for 16 h. (e) Impact of EVER2 fragments on TNF-α-induced NF-κB activation. Cells were transfected with the various EVER2 fragments and TNF-α-induced NF-κB activation was assayed as described above. Means±S.E.'s (n=3 separate experiments) are shown. Student's t-test comparing the effect of EVER2–FL with that of other EVER2 fragments: ***P<0.001; **P<0.005; *P<0.05