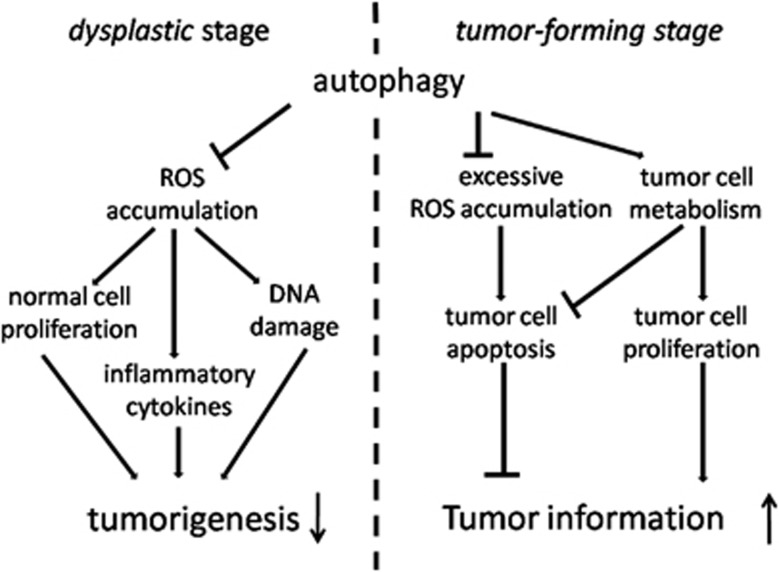
Figure 8.
Autophagy had dual role in the process of hepatocarcinoma development. In the Ds and Ts of hepatocarcinoma development, autophagy exerted different effects. In the Ds, autophagy suppressed tumorigenesis by inhibiting ROS accumulation, which resulted in concurrent increases of cell proliferation, DNA damage and inflammatory cytokines. However, in the Ts, autophagy promoted tumor formation by supporting cell proliferation and resisting cell apoptosis in tumor. In this period, autophagy inhibited excessive ROS accumulation of tumor cells, which led to cell apoptosis, and maintained tumor cell metabolism, which had pro-proliferative and anti-apoptotic properties