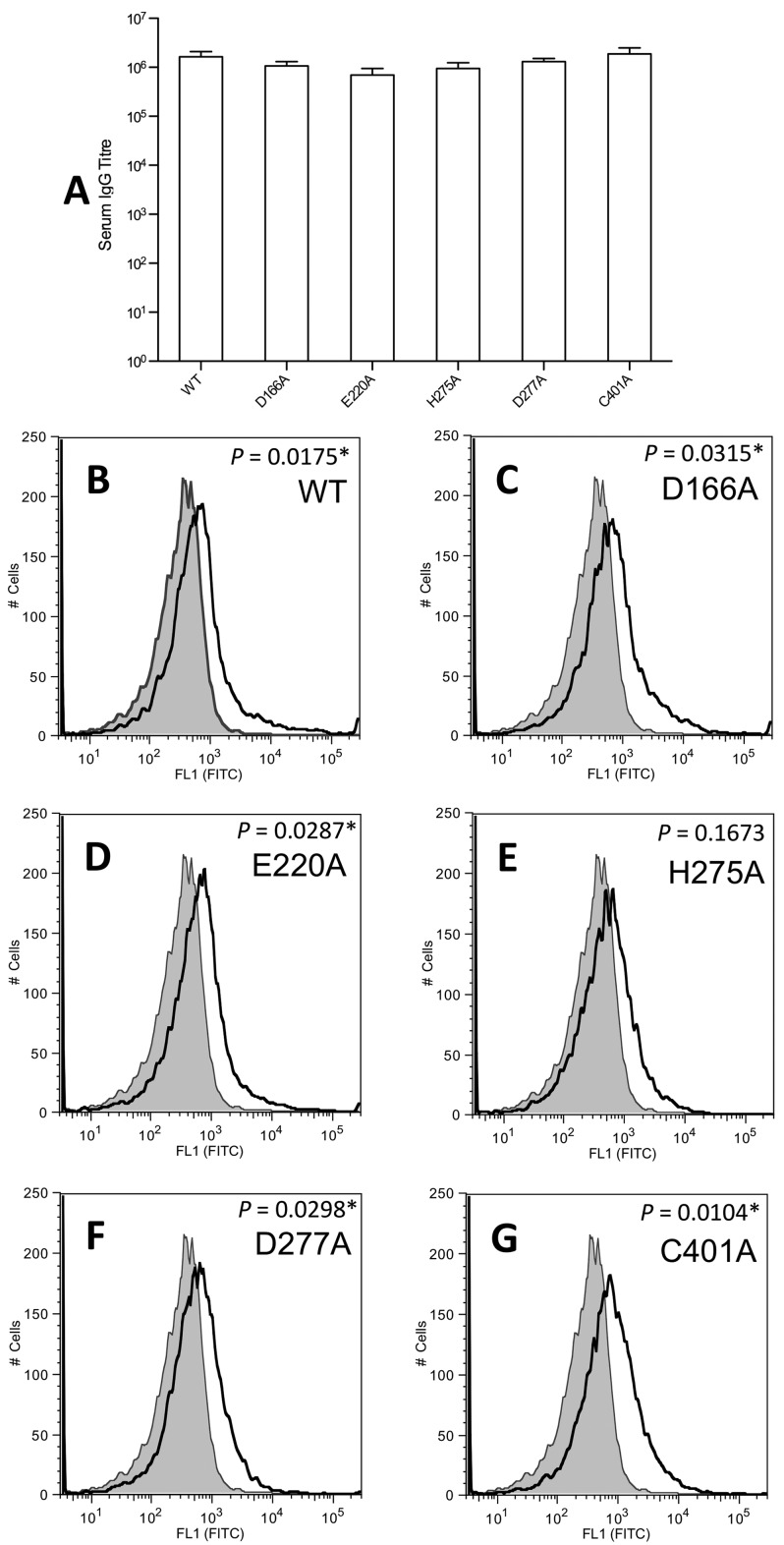
FIG 2 .
Capacity of antisera raised against mutant ADIs to recognize recombinant and native wild-type ADIs. BALB/c mice (n = 5) were immunized via the subcutaneous route with each individual ADI protein. Negative control mice were sham immunized with TBS and adjuvant only. Mice were administered 10 µg of protein on days 0, 21, and 28. Serum was collected on day 42. (A) Serum-specific IgG antibody titers determined by ELISA by using wild-type (WT) ADI to coat the plate. TBS sham serum did not produce measurable IgG titers against ADI. The absorbance cutoff for IgG titer determination was 0.2. Error bars represent the standard error of the mean. (B to G) Quantification of native ADI on the surface of GAS M1T1 isolate 5448 by flow cytometry. The histograms obtained for sera immunized with ADI proteins are indicated with a solid line; shading indicates the histogram for TBS sham serum. Panels: B, wild-type ADI; C, D166A mutant ADI; D, E220A mutant ADI; E, H275A mutant ADI; F, D277A mutant ADI; G, C401A mutant ADI. Incubation of GAS with sera raised against wild-type ADI and the D166A, E220A, D277A, and C401A mutant ADIs resulted in a significant shift in geometric mean surface fluorescence (P < 0.05; indicated by an asterisk) in comparison with that obtained with TBS sham serum. Triplicate data from two independent replicate experiments were obtained, and representative histograms are presented.