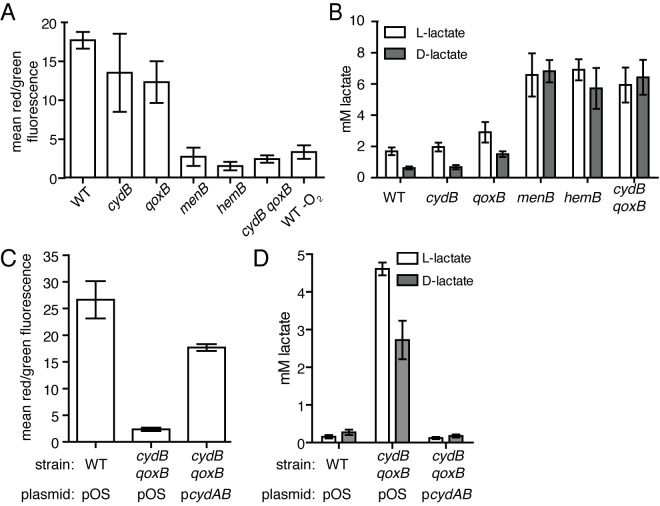
FIG 3 .
Inactivation of both cydB and qoxB limits the metabolic flexibility of S. aureus. (A) The membrane potential was measured as the mean ratio of red/green fluorescence of wild-type (WT) and mutant strains of S. aureus grown to mid-exponential phase and incubated with 30 µM of the dye 3′3′-diethyloxacarbocyanine iodide (DiOC2). The average from three independent experiments is shown. Error bars represent one standard deviation from the mean. (B) l-Lactate and d-lactate production in aerobically respiring and fermenting strains of S. aureus after 15 h of growth. The average from three independent experiments is shown. Error bars represent one standard deviation from the mean. (C) The membrane potential of wild-type (WT) S. aureus and the qoxB cydB mutant harboring a plasmid control (pOS) or a plasmid containing the cydAB operon (pcydAB) was measured as the mean ratio of red/green fluorescence when the strains were grown to mid-exponential phase and incubated with 30 µM of the dye 3′3′-diethyloxacarbocyanine iodide (DiOC2). The average from three independent experiments is shown. Error bars represent one standard deviation from the mean. (D) l-Lactate and d-lactate produced in the supernatants of wild-type (WT) S. aureus and the qoxB cydB mutant harboring a plasmid control (pOS) or a plasmid containing the cydAB operon (pcydAB) grown after 12 h of growth. The average from three independent experiments is shown. Error bars represent one standard deviation from the mean.