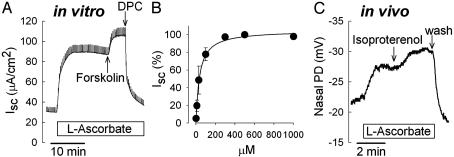
Fig. 2.
Stimulation of Cl transport by l-ascorbate. (A) Measurement of transepithelial Cl secretion (Isc) across Calu-3 airway epithelia in vitro. l-ascorbate (100 μM, mucosal) stimulated Isc in a sustained fashion. Ascorbate-stimulated CI secretion is further increased by forskolin (20 μM, serosal) and completely inhibited by the Cl channel blocker DPC (4 mM). (B) Dose-dependency of ascorbate-stimulated Cl currents. Half-maximal stimulatory constant averaged 36.5 ± 2.9 μM (n = 14). (C) Measurement of NPD in a human subject in vivo. Perfusion of the nasal floor with l-ascorbate (300 μM) hyperpolarized NPD. Response to the β-adrenergic agonist isoproterenol (10 μM) is shown for comparison. wash, Washout with saline.