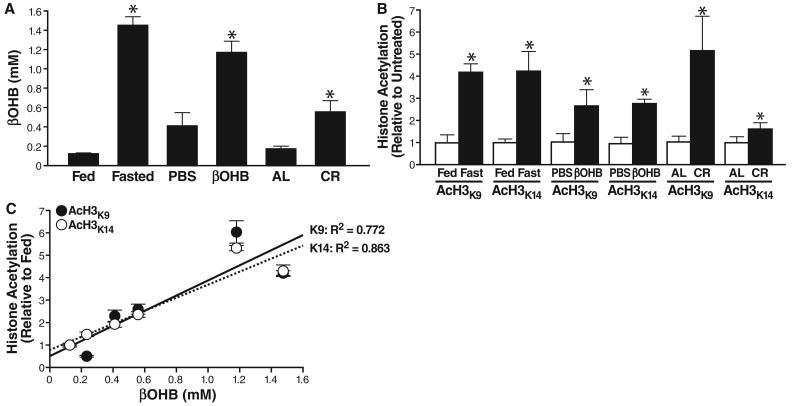
Fig. 2.
Serum βOHB and global histone acetylation in kidney of mice deprived of food. (A) Serum concentration of βOHB was determined in age-matched groups of three C57Bl6 mice fed or fasted (16 weeks old, fasted for 24 hours), implanted with a pump delivering either PBS or βOHB (16 weeks old, 24 hours of pump treatment), fed ad libitum (AL) or on calorie restriction to 60% of AL (CR) (8 months old, 6 months on CR). Mean ± SE, *P < 0.05 by t test between paired conditions. (B) Histones were purified from the kidneys of the same mice as in (A). Acetylation was assessed with anti-AcH3K9, anti-AcH3K14, or anti-Ac-α-tubulin (fig. S8). Acetylation is normalized to total histone H3 and shown relative to the control condition in each pair (e.g., fed versus fasted). Mean ± SE, *P < 0.05 by t test between paired conditions. (C) Serum βOHB concentrations [from (A)] plotted against acetylation of histone H3K9 and H3K14 [from (B)]; correlation coefficient R2 = 0.772 for H3K9 and 0.863 for H3K14.