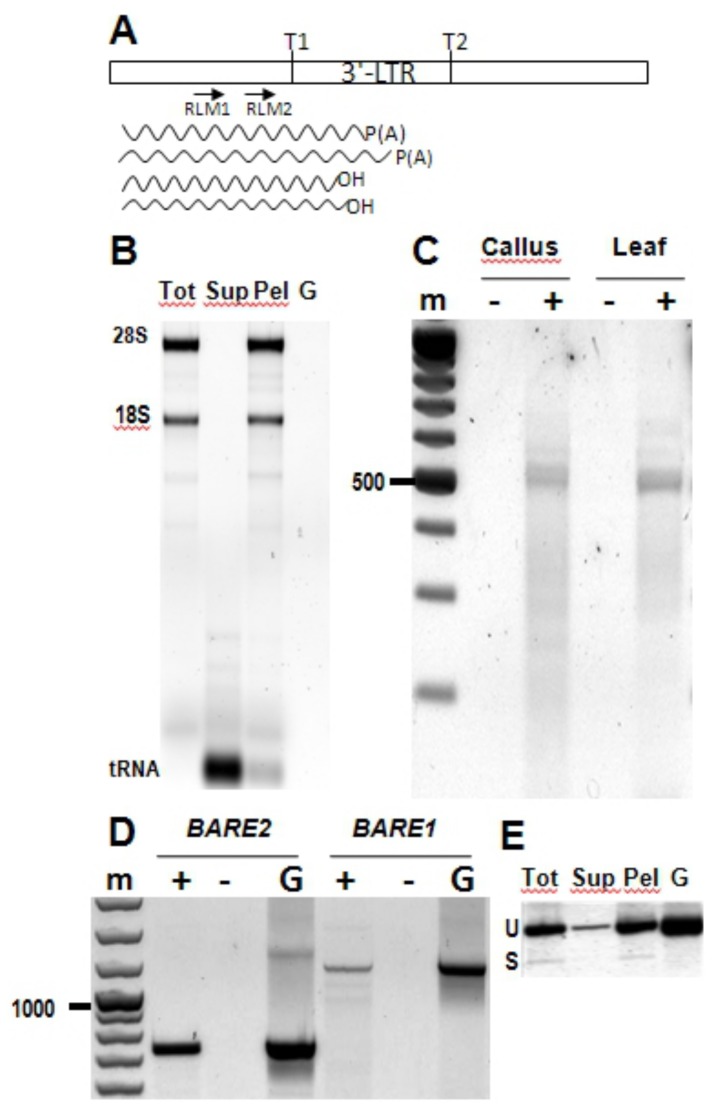
Figure 4. Spliced BARE RNA is associated with polyribosomes.
A. Diagram of the 3’ LTR, indicating for reference the position of the two TATA boxes TATA1 (T1) and TATA2 (T2); only those in the 5’ LTR serve to transcribe the retrotransposon. The positions of forward primers RLM1 and RLM2 for 3’ RLM-RACE are shown. The wavy lines show, respectively, the approximate termination positions of the polyribosome-associated poly(A) RNA. B. Supernatant (Sup) and polyribosome pellet (Pel) fractions from total callus RNA (Tot) ultracentrifuged on a 10-45% sucrose gradient. rRNA bands are labelled. C. Electrophoresis of RLM-RACE reactions from polyribosome-associated callus and leaf RNA amplifying both BARE1 and BARE2. A 100 bp size ladder (m) is shown, 500 bp marked. D. Amplification of BARE2 and BARE1 from polyribosome-associated callus RNA (primers 1965 and 1966 for BARE2, primers Gag5 and AP4 for BARE1, Figure 2). Negative controls (-) for the presence of genomic DNA contamination lack reverse transcriptase; positive controls, G, contain genomic DNA. Bars point to 1000 bp and 500 bp size markers, m. E. RT-PCR assay (primers F1594 and F1593, Figure 2, which are not specific to BARE1) from the fractions in (B). For size comparison, PCR from genomic DNA with the same primers is shown on the right. Unspliced and spliced transcripts are indicated as U and S, respectively. The RT-minus controls gave no amplification.