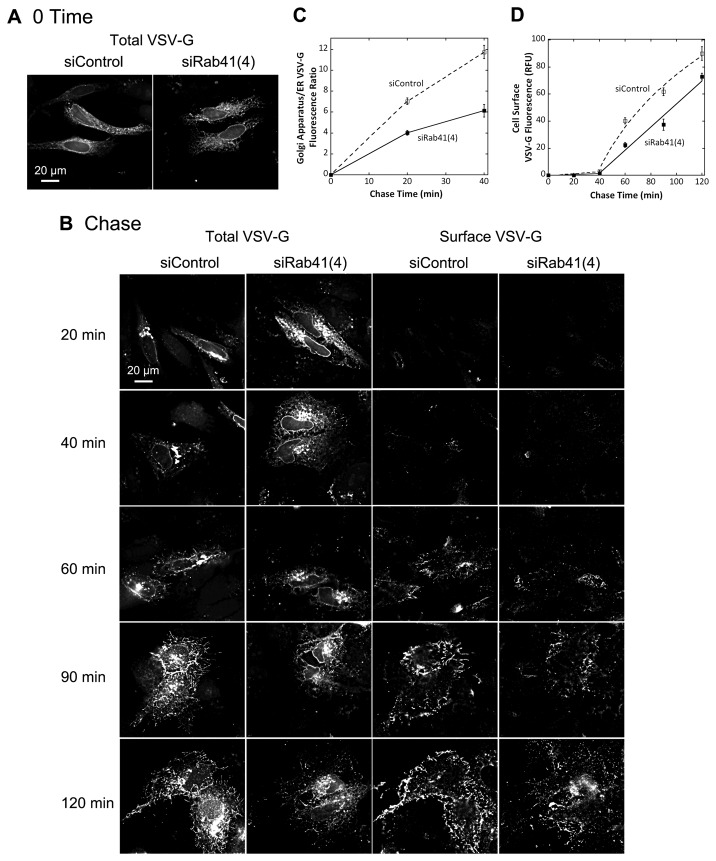
Figure 7. Depletion of Rab41 partially inhibited VSV-G transport from ER to the cell surface with a significant inhibition of ER to Golgi transport.
Wild type HeLa cells were incubated with either siRab41(4) or non-targeting siRNA duplexes for 96 h and then transfected with plasmid encoding VSV-G-GFP. At the end of the 39.5° C incubation period, VSV-G was accumulated in the ER (A). Cells were then shifted to 32° C, permissive conditions for VSV-G transport, and incubated for various chase time in the presence of cycloheximide to prevent further protein synthesis (B). Cells were then fixed and cell surface stained for VSV-G, and visualized by wide field light microscopy. At the end of a 20-min chase or 40-min chase, Golgi accumulation of VSV-G was observed in both control and Rab41 knockdown cells. However, VSV-G retention in the ER of Rab41 depleted cells was decidedly higher than that of control cells (total VSV-G, left two columns in B, and C). Consistently, at later chase times, surface accumulation of VSV-G in Rab41 knockdown cells was quantitatively slower than that in control cells (surface VSV-G, right two columns in B, and D). All images shown or used for quantification were single-plane deconvolved. Error bars are the mean ± St Dev of three independent experiments. ~30 cells were assayed for each time point in the individual experiments.