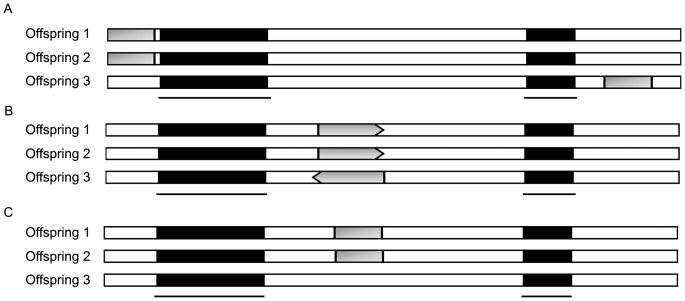
Figure 8. Schematic representation of the possible outcomes of genomic recombination in organisms with frequent recombination.
(A) Conserved sequences (represented by dark rectangles) in the offspring genomes are separated by foreign segments (represented by empty blocks) as a result of multiple insertion events. (B) Recombination and inversion might occur in the offspring genomes and lead to positional and directional rearrangement of the conserved region (represented by dark arrows; the arrowhead indicates the direction). (C) Progeny genomes can share similar genome organization, but certain distinctive segments (represented by gray rectangles) within these regions can be shared only by a subset of the progeny.