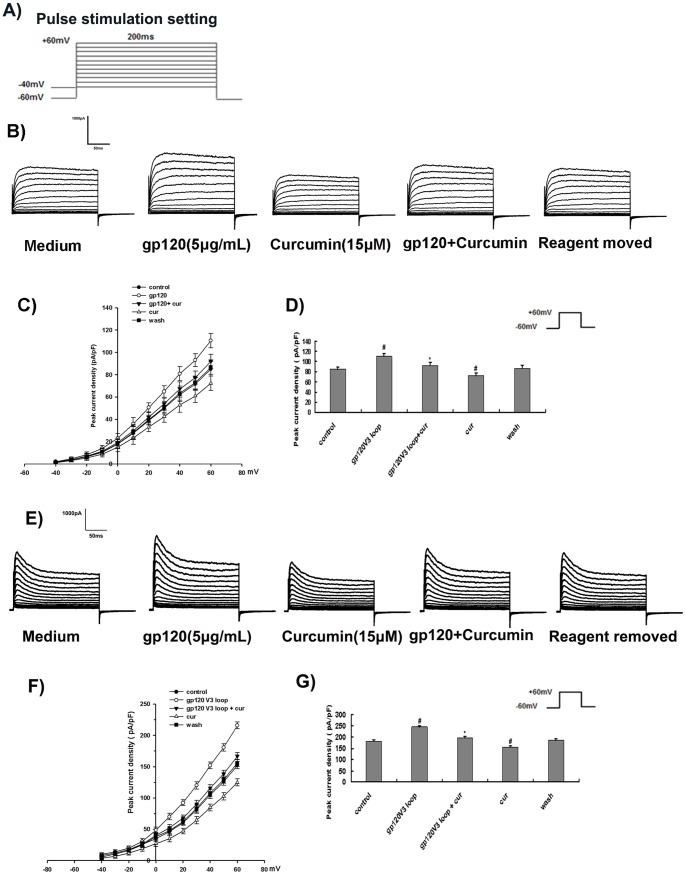
Figure 5. Curcumin attenuated HIV-1 gp120 V3 loop-induced increase in the delayed rectifier K+ current and the transient outward K+ current.
Whole-cell patch clamp recordings of primary rat cortical neuronal bioactivity in response to gp120 (5 µg/mL) treatment with or without curcumin (15 µM) were performed in 35-mm culture dishes on an inverted Olympus microscope stage using an Axopatch 200B amplifier. Whole-cell delayed rectifier K+ current and transient outward K+ current were induced through voltage steps ranging from −60 mV to +60 mV in 10-mV increments. A): Schematic representation of the pulse stimulation setting for both recordings of delayed rectifier K+ current and transient outward K+ current. B): A recording of delayed rectifier potassium current in medium (control), cells treated with gp120 (5 µg/mL), curcumin (15 µM),gp120 (5 µg/mL) plus curcumin (15 µM), or post-washing. C): I-V curves of delayed rectifier K+ current densities in response to gp120 (5 µg/mL) treatment with or without curcumin (15 µM). D): Pooled whole-cell recording data of the delayed rectifier K+ current from 6 separated experiments. E): A recording of transient outward K+ current in medium (control), cells treated with gp120 (5 µg/mL), curcumin (15 µM),gp120 (5 µg/mL) plus curcumin (15 µM), or post-washing. F: I–V curves of transient outward K+ current densities in response to gp120 (5 µg/mL) treatment with or without curcumin (15 µM). G: Pooled whole-cell recording data of the transient outward K+ current from 6 separated experiments. Each value represents the mean ± SEM. #, p<0.05 vs. control; *, p<0.05 vs. HIV-1 gp120 V3 loop alone; n = 6.