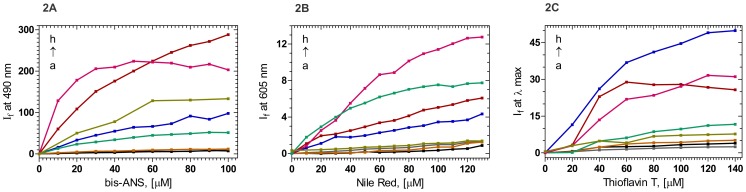
Figure 2. A:Surface exposure of residues in the proteins, monitored using bis-ANS as the extrinsic probe.
A (Black): WT; B (Grey): P24T; C (Brown): R77S; D (Green):Y134A; E (Blue): G165fs; F (Olive): A36P; G (Violet): L45PL54P; and H (Maroon): R140X. If at 490 nm of the probe was measured as a function of its increasing concentration λexc: 390 nm, cell path length 3 mm, excitation and emission slits 2.5 nm. Each curve is an average of 3 independent runs. B: Aggregation tendencies of the proteins, estimated using Nile Red as the extrinsic probe. A (Black): WT; B (Brown): R77S; C (Grey): P24T; D (Olive): A36P; E (Blue): G165fs; F (Maroon): R140X; G (Green): Y134A; and H (Violet): L45PL54P. If at 605 nm of the probe was measured as a function of its increasing concentration. λexc: 540 nm, cell path length 3 mm, excitation emission slits 10 nm. Each curve is an average of 3 independent runs. C: Using Thioflavin-T to probe amyloid-type aggregation of HGDC and its mutants. A (Grey): P24T; B (Black): WT; C (Brown): R77S; D(Olive): A36P; E (Green): Y134A; F (Maroon): R140X; G (Violet): L45PL54P; and H (Blue): G165fs. If of the probe at λmax was measured as a function of increasing concentration. Protein concentration in each case was fixed at 6 µM, cell path length 3 mm, excitation and emission slits 5 nm. Each curve is an average of 3 independent runs.