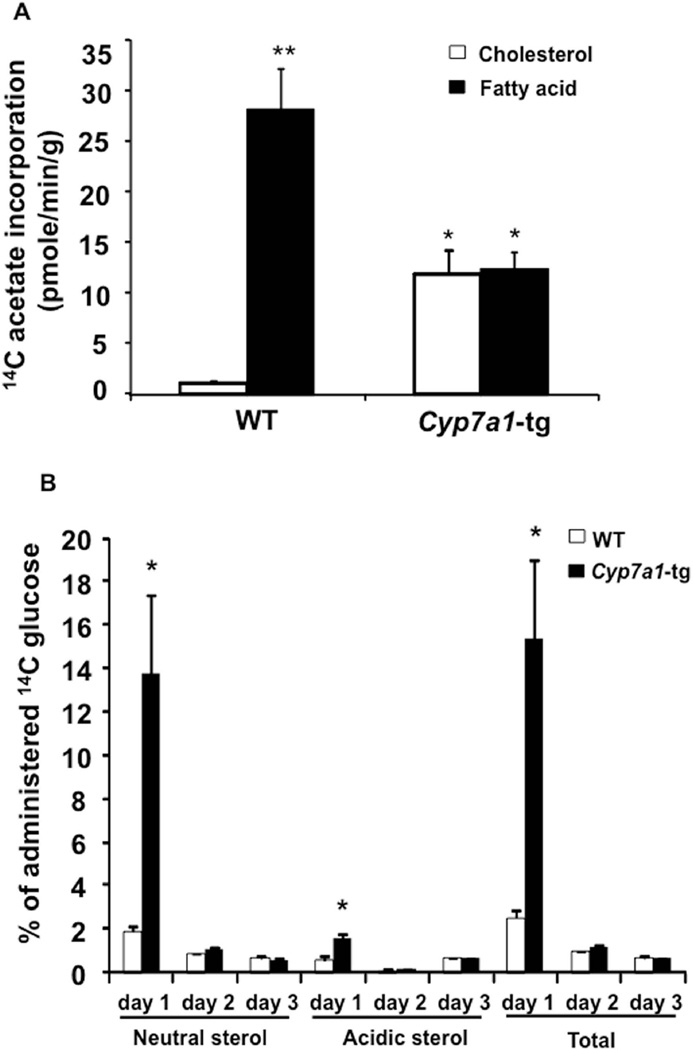
Figure 1. Cyp7a1-tg mice have increased cholesterol synthesis and decreased fatty acid synthesis in the liver.
A. Hepatic cholesterol and fatty acid synthesis rates were measured as described in Materials and Methods. The activities of 3H and 14C were determined in a scintillation counter. The cholesterol and fatty acid synthesis rates were expressed as 14C radioactivity derived from 14C-acetate (adjusted by internal recovery standard 3H-cholesterol radioactivity) and incorporated into cholesterol or fatty acids per minute per gram liver tissue. B. Wild type and Cyp7a1-tg mice were ip. injected with a single dose of glucose (8 g/kg) containing 5 µCi [1-14C] glucose, and fecal 14C sterol amount was estimated as described in Materials and Methods. The fecal acidic sterols (bile acids) and neutral sterols (cholesterol) derived from 14C-glucose were estimated by measuring the radioactivity of 14C incorporated, adjusted by internal standard 3H-cholesterol radioactivity, and expressed as percentage of total administrated 14C activity. Results are expressed as mean ± SE; “*” indicates p < 0.05 vs. WT. “**” indicates p < 0.05 vs. 14C incorporation into cholesterol in WT mice, n = 4-5.